简介
A
android资源之res/raw和assets的异同
■ res/raw和assets的相同点:
两者目录下的文件在打包后会原封不动的保存在apk包中,【不会被编译成二进制】。
■ res/raw和assets的不同点:
1、res/raw中的文件会被映射到R.java文件中,访问的时候直接使用资源ID即R.id.filename;assets文件夹下的文件不会被映射到R.java中,访问的时候需要AssetManager类
2、res/raw不可以有目录结构,而assets则可以有目录结构,也就是assets目录下可以再建立文件夹
■ 读取文件资源:
1、读取res/raw下的文件资源,通过以下方式获取输入流来进行写操作
InputStream is = getResources().openRawResource(R.id.filename);
2、读取assets下的文件资源,通过以下方式获取输入流来进行写操作
AssetManager am = null;
am = getAssets();
InputStream is = am.open("filename");
am.close(); //关闭AssetManager
ADB命令对包 com.zukgit 进行 100次测试
adb shell monkey -p com.zukgit -v 100
adb shell monkey -p net.micode.fileexplorer -v 100
AIDL(HAIL接口 AIDL化 )
传统 HAL 接口(如 HIDL)的升级需要同时修改 Framework 和 HAL 实现,导致耦合度高,阻碍系统升级 。
Google 在 Android 8 引入 Treble 计划时,通过 HIDL 解耦了 Framework 和 HAL,但 HIDL 仍需通过 Binder IPC 进行跨进程通信。
而 AIDL 进一步简化了这一流程,允许 APP 直接通过 AIDL 与 HAL 通信(如 APP → AIDL → HAL),
减少中间环节(如 HIDL 的 APP → AIDL → System → HIDL → HAL 路径),提升了效率 。
此外,AIDL 支持更灵活的版本控制,无需重新编译接口即可扩展功能 。
HIDL接口原始调用路径
( APP → AIDL → System → HIDL → HAL)
HIDL接口AIDL化之后
( APP → AIDL → HAL)
优点:
1.允许 APP 直接通过 AIDL 与 HAL 通信 ,减少了跨进程调度开销,提高响应速度 降低系统资源消耗
2.AIDL 支持更灵活的版本控制,无需重新编译接口即可扩展功能( 解耦合 达到谷歌单独更新系统核心组件的目的)
3.资源利用效率提升, AIDL服务在客户端数量为0时可自动退出,节省内存资源;而HIDL服务通常常驻内存
| 维度 | HIDL | AIDL化优势 |
|---|---|---|
| IPC机制 | 依赖HwBinder,需跨System进程 | 统一Binder,直通HAL减少中间层 |
| 版本控制 | 需创建新版本目录(如@1.1) | 直接扩展接口,无需冗余目录 |
| 资源占用 | 服务常驻内存 | 按需加载,自动退出节省资源 |
| 开发体验 | C++语法,学习成本高 | Java语法,工具链成熟 |
| 性能 | 单层性能可能更高,但整体路径更长 (APP → AIDL → System → HIDL → HAL) | 通信路径缩短,错误处理更稳定 (APP → AIDL → HAL) |
| 未来支持 | 不再新增API,逐步废弃 | 新功能仅支持AIDL,长期兼容性更佳 |
AsyncTask——实现异步任务
AsyncTask------实现异步任务
提到异步任务,我们能想到用线程,线程池去实现.确实,Android给我们提供了主线程与其他线程通讯的机制.
但同时,Android也给我们提供了一个封装好的组件--AsyncTask.
利用AsyncTask,我们可以很方便的实现异步任务处理.AsyncTask可以在子线程中更新UI,也封装简化了异步操作.使用线程,线程池处理异步任务涉及到了线程的同步,管理等问题.
AsyncTask<Params,Progress,Result>是一个抽象类,通常用于被继承.继承AsyncTask需要指定如下三个泛型参数:
Params:启动任务时输入的参数类型.
Progress:后台任务执行中返回进度值的类型.
Result:后台任务执行完成后返回结果的类型.
doInBackground:必须重写,异步执行后台线程要完成的任务,耗时操作将在此方法中完成.
onPreExecute:执行后台耗时操作前被调用,通常用于进行初始化操作.
onPostExecute:当doInBackground方法完成后,系统将自动调用此方法,并将doInBackground方法返回的值传入此方法.通过此方法进行UI的更新.
onProgressUpdate:当在doInBackground方法中调用publishProgress方法更新任务执行进度后,将调用此方法.通过此方法我们可以知晓任务的完成进度.
public class ImageActivity extends Activity {
private ImageView imageView ;
private ProgressBar progressBar ;
private static String URL = "http://pic3.zhongsou.com/image/38063b6d7defc892894.jpg";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.image);
imageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
progressBar = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.progressBar);
//通过调用execute方法开始处理异步任务.相当于线程中的start方法.
new MyAsyncTask().execute(URL);
}
class MyAsyncTask extends AsyncTask<String,Void,Bitmap> {
//onPreExecute用于异步处理前的操作
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
super.onPreExecute();
//此处将progressBar设置为可见.
progressBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
//在doInBackground方法中进行异步任务的处理.
@Override
protected Bitmap doInBackground(String... params) {
//获取传进来的参数
String url = params[0];
Bitmap bitmap = null;
URLConnection connection ;
InputStream is ;
try {
connection = new URL(url).openConnection();
is = connection.getInputStream();
//为了更清楚的看到加载图片的等待操作,将线程休眠3秒钟.
Thread.sleep(3000);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
//通过decodeStream方法解析输入流
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(bis);
is.close();
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bitmap;
}
//onPostExecute用于UI的更新.此方法的参数为doInBackground方法返回的值.
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(Bitmap bitmap) {
super.onPostExecute(bitmap);
//隐藏progressBar
progressBar.setVisibility(View.GONE);
//更新imageView
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
}
}
}
activemq消息队列库
ActiveMQ 是Apache出品,最流行的,能力强劲的开源消息总线。
代码说明: https://www.cnblogs.com/jaycekon/p/6225058.html
apollo: https://activemq.apache.org/apollo/
Multi-protocol messaging broker based on ActiveMQ
以activemq实现的消息收发框架
ActiveMQ官网下载地址:http://activemq.apache.org/download.html
一、ActiveMQ核心概念
1、ActiveMQ是消息队列技术,为解决高并发问题而生!
2、ActiveMQ生产者消费者模型(生产者和消费者可以跨平台、跨系统)
有中间平台
3、ActiveMQ支持两种消息传输方式
1)Queue,队列模式,生产者生产了一个消息,只能由一个消费者进行消费
2)Topic,发布/订阅模式,生产者生产了一个消息,可以由多个消费者进行消费
特性:
1. 多种语言和协议编写客户端。语言: Java,C,C++,C#,Ruby,Perl,Python,PHP。应用协议: OpenWire,Stomp REST,WS Notification,XMPP,AMQP
2.完全支持JMS1.1和J2EE 1.4规范 (持久化,XA消息,事务)
B
C
CountDownLatch 同步辅助类
一个同步辅助类,在完成一组正在其他线程中执行的操作之前,它允许一个或多个线程一直等待。
用给定的计数 初始化 CountDownLatch
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class CountDownLatchTest {
/**
**
* step.1 创建CountDownLatch 实例 预定计数次数:10
* CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(10);
**
*
* step.2 递减锁存器的计数,如果计数到达零,则释放所有等待的线程。 如果当前计数大于零,则将计数减少 1
* latch.countDown();
*
*
* step.3 使当前线程在锁存器倒计数至零之前一直等待,除非线程被中断 如果当前的计数为零,则此方法立即返回
* latch.await();
**/
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int count = 10; // 计数次数
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// do anything
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (Throwable e) {
// whatever
} finally {
// 很关键, 无论上面程序是否异常必须执行countDown,否则await无法释放
latch.countDown();
}
}
}).start();
}
try {
// 10个线程countDown()都执行之后才会释放当前线程,程序才能继续往后执行
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// whatever
}
System.out.println("Finish");
}
}
/*
输出:
线程Thread-0
线程Thread-5
线程Thread-4
线程Thread-8
线程Thread-1
线程Thread-3
线程Thread-2
线程Thread-9
线程Thread-7
线程Thread-6
Finish
*/
D
E
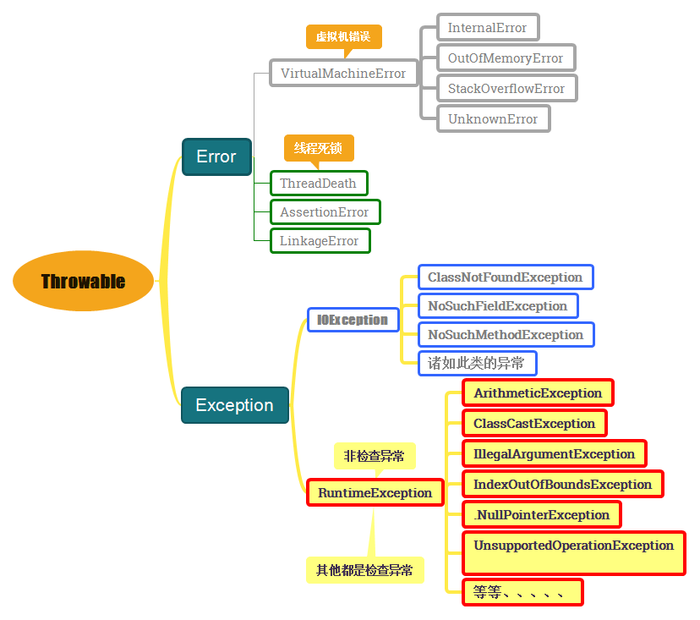
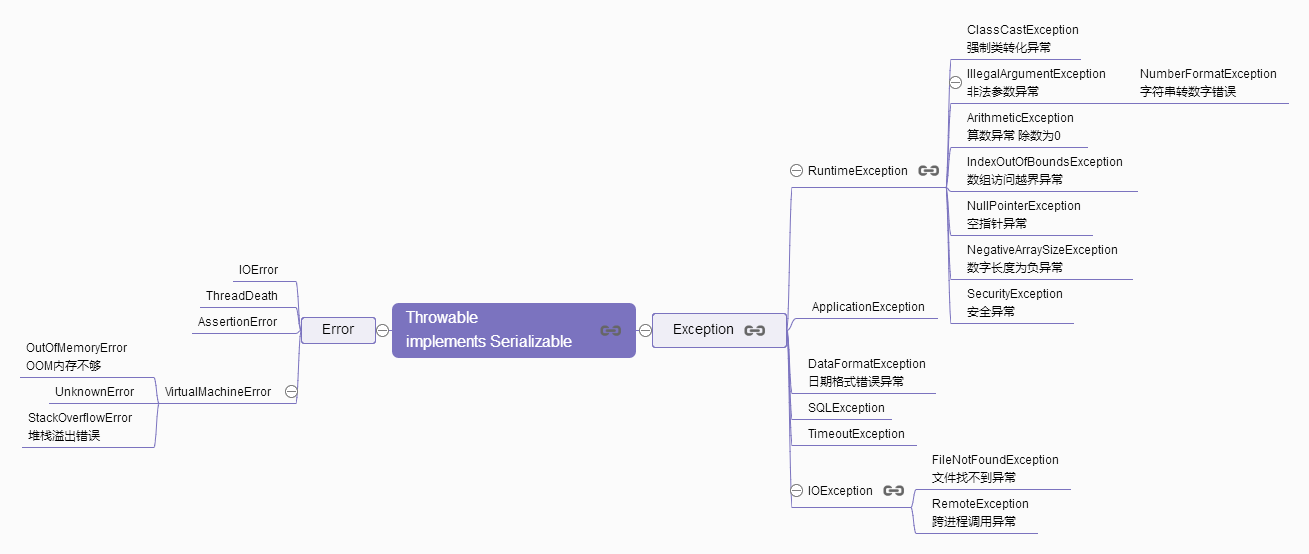
Error 与 Exception
Exception(异常 通常程序员造成) 分为:
1.检查异常: (编写源代码时需要显示的进行处理,在方法中try或者throws)
2.不检查异常 (运行时异常,如: NullPointerException 空指针 、io FileNotFoundException 异常,数组越界 IndexOutOfBoundsException )
(ArithmeticException 算术运算异常 , IllegalArgumentException 传递非法参数异常 , NumberFormatException 数字格式异常 )
(NegativeArraySizeException 创建一个大小为负数的数组错误异常 , ClassCastException 类型强制转换异常 )
java中关于对异常和错误的处理:
有一个顶层的父类 Throwable。一个对象只有是 Throwable 类的(直接或者间接)实例,他才是一个异常对象,才能被异常处理机制识别。
public class Exception extends Throwable {}
public class Error extends Throwable {}
public class Throwable implements Serializable {}
Error (错误 系统层面 一般系统层面):
程序员无法通过程序改变的错误,多为jvm本身的错误。如堆溢出错误、栈溢出错误
实践应用:
尽量不要捕获类似 Exception 这样的通用异常,而是应该捕获特定异常
不要生吞(swallow)异常。
了解一下Throw early, catch late 原则(早点抛出异常延迟抓取异常)
【即 catch的顺序必须是子类RuntimeException必须在前 父类Exception在后 如果父类Exception在前 那么会报错 ,试用所有Error Exception】
性能方面来说:尽量不要一个大的 try 包住整段的代码、,利用异常控制代码流是影响效率的
| 类名 | 说明 | |
|---|---|---|
| ClassCastException | 类型强制转换异常 | |
| ArithmeticExecption | 算术异常类 | |
| NegativeArrayException | 数组负下标异常 | |
| ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException | 数组下标越界异常 | |
| NumberFormatException | 字符串转换为数字异常 | |
| FileNotFoundException | 文件未找到异常 | |
| EOFException | 文件已结束异常 | |
| SecturityException | 违背安全原则异常 | |
| SQLException | 操作数据库异常 | |
| IOException | 输入输出异常 | |
| NoSuchMethodException | 方法未找到异常 | |
| AbstractMethodError | 抽象方法错误。当应用试图调用抽象方法时抛出 | |
| AssertionError | 用来指示一个断言失败的情况 | |
| ClassCircularityError | 在初始化一个类时,若检测到类之间循环依赖则抛出该异常 | |
| ClassFormatError | 文件的内容不符合类的有效格式时抛出 | |
| Error | 错误 是所有错误的基类 用于标识严重的程序运行问题 | |
| Exception | InInitializerError 初始化程序错误 | |
| IllegalAccessError | 非法参数 违法访问错误 当一个应用试图访问 、修改某个类的域(Field)或者调用其方法,但是又违反域或方法的可见性声明 | |
| IncompatibleClassChangeError | 不兼容的类变化错误 当正在执行的方法所依赖的类定义发生了不兼容的改变时 抛出该异常 | |
| InstantiationError | 实例化错误 new操作符构造一个抽象类或者接口时抛出该异常 | |
| InternalError | 内部错误 用于指示 java虚拟机发生了内部错误 | |
| LinkageError | 链接错误 该错误及其所有子类指示某个类依赖于另外一些类 在该类编译之后 被依赖的类改变了其类定义而没有重新编译所有的类 | |
| NoClassDefFoundError | 未找到类定义错误 | |
| NoSuchFieldError | 域不存在错误 该类的定义中没有该域的定义时抛出该错误 | |
| NoSuchMethodError | 方法不存在错误 | |
| OutOfMemoryError | 内存不足错误 | |
| StackOverflowError | 堆栈溢出错误 | |
| ThreadDeath | 线程结束 当调用Thread类的stop方法时抛出该错误 用于指示线程结束 | |
| UnknownError | 未知错误 java 虚拟机发生了未知严重错误的情况 | |
| UnsatisfiedLinkError | 未满足的链接错误 java虚拟机未找到某个类的声明为native方法的本机语言定义时抛 | |
| UnsupportedClassVersionError | 不支持的类版本错误 | |
| VerifyError | 验证错误 | |
| VirtualMachineError | 虚拟机错误 继续执行操作所需的资源不足的情况 | |
| RuntimeException | 是那些可能在 Java 虚拟机正常运行期间抛出的异常的超类可能在执行方法期间抛出但未被捕获的RuntimeException | 的任何子类都无需在throws子句中进行声明 |
| ClassNotFoundException | 找不到数据库驱动类 | |
| CloneNotSupportedException | 克隆 不支持 | |
| InterruptedException | 线程被中断异常 | |
| StringIndexOutOfBoundsException | 字符串越界 | |
| UnsupportedOperationException | 该操作不被支持,如果我们希望不支持这个方法,可以抛出这个异常 | |
| IllegalStateException | 非法状态 |
Demo推导出的结论:
1. catch的顺序必须是子类RuntimeException必须在前 父类Exception在后 如果父类Exception在前 那么会报错 ,试用所有Error Exception
2. Error 和 Exception 都可以捕获,它们可以混搭捕获,但必须依据 子类在前原则
3. try 出现了Exception 之后 try{} 包含的代码块就会停止执行, 然后执行 对应的 Catch 和 finally方法 ,然后执行 try{}finally{}代码块之后的代码
4. try 语句不能单独出现 必须 伴随着 try-catch try-finally try-catch-finally 三种形式出现,单独出现报错
5. 只要 try语句中包含finally 那么 不管是否在try语句中发生 Exception Error 或者 在try 语句中有 return ,只要程序不退出程序System.exit(0),那么都会在 return 执行去执行 finally语句
6. 当try或者catch的代码在运行的时候,JVM退出了 如System.exit(0) 。那么finally语句块就不会执行。
如果线程在运行try或者catch的代码时被中断了或者被杀死了(killed),那么finally语句可能也不会执行了
7. 如果程序抛出的异常没有被catch , 或者 该异常为子类 对应的 父类继承链 的所有家族类 都没有在catch 集合中 那么 程序在执行完 finally 后会 默认退出【即 System.exit(0)】
抛出异常的try{} 后面的代码得不到执行 【 例子: 如下 ClassCastExceptionDemo 】
NumberFormatException:
public class NumberFormatExceptionDemo {
static int intValue = 1;
public void MethodTryCatchFinally() {
try {
} catch (Exception e) {
}
try {
} finally {
}
}
public static int MethodTryExit() {
int x = 1;
try {
System.out.println("============= MethodTryExit try begin =============");
System.exit(0);
System.out.println("============= MethodTryExit try end =============");
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
System.out.println("============= MethodTryExit finally begin =============");
++x;
System.out.println("============= MethodTryExit finally end x="+x + "=============");
}
return x;
}
public static int MethodTryReturn() {
int x = 1;
try {
System.out.println("============= MethodTryReturn try begin =============");
return ++x;
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
System.out.println("============= MethodTryReturn finally begin =============");
++x;
System.out.println("============= MethodTryReturn finally end x="+x + "=============");
}
return x;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("============= main begin =============");
int valueA = MethodTryReturn();
try {
System.out.println("============= try begin =============");
intValue = Integer.parseInt("ABC");
System.out.println("============= try end intValue=" + intValue);
System.out.println("============= try end =============");
return;
}
catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
System.out.println("============= catch OutOfMemoryError begin =============");
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("============= catch OutOfMemoryError end =============");
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("============= catch NumberFormatException begin =============");
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("============= catch NumberFormatException end =============");
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.out.println("============= catch IllegalArgumentException begin =============");
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("============= catch IllegalArgumentException end =============");
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
System.out.println("============= catch RuntimeException begin =============");
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("============= catch RuntimeException end =============");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("============= catch Exception begin =============");
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("============= catch Exception end =============");
}
catch (Error e) {
System.out.println("============= catch Error begin =============");
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("============= catch Error end =============");
}
finally {
System.out.println("============= finally begin =============");
intValue = 0;
System.out.println("============= finally end =============");
}
int valueB = MethodTryExit();
System.out.println("============= main end-intValue =" + intValue);
System.out.println("============= main end =============");
}
}
/**
输出:
============= main begin =============
============= MethodTryReturn try begin =============
============= MethodTryReturn finally begin =============
============= MethodTryReturn finally end x=3=============
============= try begin =============
============= catch NumberFormatException begin =============
java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "ABC"
at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Unknown Source)
at test.NumberFormatExceptionDemo.main(NumberFormatExceptionDemo.java:64)
============= catch NumberFormatException end =============
============= finally begin =============
============= finally end =============
============= MethodTryExit try begin =============
**/
ClassCastException extends RuntimeException 【强制转化异常】
public class ClassCastExceptionDemo {
public static void MethodCatch(int index) {
System.out.println("=============MethodCatch begin=============");
try {
if (index > 100)
throw new NumberFormatException("超过数组长度越界");
}
catch(RuntimeException e) {
System.out.println("=============MethodCatch catch begin=============");
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("=============MethodCatch catch end=============");
}
finally {
System.out.println("=============MethodCatch finally begin=============");
System.out.println("=============MethodCatch finally end=============");
}
System.out.println("=============MethodCatch end=============");
}
public static void MethodNoCatch(int index) {
System.out.println("=============MethodNoCatch begin=============");
try {
if (index > 100)
throw new NumberFormatException("超过数组长度越界");
}
catch(NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("=============MethodNoCatch catch begin=============");
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("=============MethodNoCatch catch begin=============");
}
finally {
System.out.println("=============MethodNoCatch finally begin=============");
System.out.println("=============MethodNoCatch finally end=============");
}
System.out.println("=============MethodNoCatch end=============");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("============== main begin ==============");
MethodCatch(101);
try {
System.out.println("============== main try begin ==============");
Object x = new Integer(0);
System.out.println((String) x);
System.out.println("============== main try end ==============");
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("============== main finally begin ==============");
System.out.println("============== main finally end ==============");
}
MethodNoCatch(101);
System.out.println("============== main end ==============");
}
}
/*
输出:
============== main begin ==============
=============MethodCatch begin=============
=============MethodCatch catch begin=============
java.lang.NumberFormatException: 超过数组长度越界
at test.ClassCastExceptionDemo.MethodCatch(ClassCastExceptionDemo.java:9)
at test.ClassCastExceptionDemo.main(ClassCastExceptionDemo.java:45)
=============MethodCatch catch end=============
=============MethodCatch finally begin=============
=============MethodCatch finally end=============
=============MethodCatch end=============
============== main try begin ==============
java.lang.ClassCastException: java.lang.Integer cannot be cast to java.lang.String
at test.ClassCastExceptionDemo.main(ClassCastExceptionDemo.java:50)
============== main finally begin ==============
============== main finally end ==============
=============MethodNoCatch begin=============
=============MethodNoCatch finally begin=============
=============MethodNoCatch finally end=============
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: 超过数组长度越界
at test.ClassCastExceptionDemo.MethodNoCatch(ClassCastExceptionDemo.java:28)
at test.ClassCastExceptionDemo.main(ClassCastExceptionDemo.java:58)
*/
java中异常抛出后代码还会继续执行吗:
总结:
若一段代码前有异常抛出,并且这个异常没有被捕获,这段代码将产生编译时错误「无法访问的语句」。
若一段代码前有异常抛出,并且这个异常被try...catch所捕获 父子链成员补货,若此时catch语句中没有抛出新的异常,则这段代码能够被执行,否则,同第1条。如代码2
若在一个条件语句中抛出异常,则程序能被编译,但后面的语句不会被执行。如代码3
F
foreach and delete
不要在 foreach 循环里进行元素的 remove/add 操作。否则可能会出现ConcurrentModificationException
remove 元素请使用 Iterator方式,如果并发操作,需要对 Iterator 对象加锁。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class F {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
for (String item : list) {
if ("2".equals(item)) {
list.remove(item);
}
}
}
}
报错:
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.checkForComodification(Unknown Source)
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.next(Unknown Source)
at F.main(F.java:15)
正确的遍历删除操作 使用 Iterator
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class F {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String item = iterator.next();
if ("2".equals(item)) {
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
G
GC
虚拟机中的共划分为三个代:年轻代(Young Generation)、老年代(Old Generation)和持久代(Permanent Generation)
H
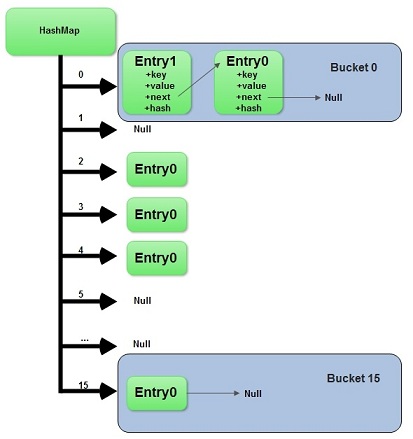
HashMap的数据结构
HashMap 产生的缘由: 要了解 HashMap 产生的缘由 先了解 数组和链表各自的特点:
数组的特点是:寻址容易,插入和删除困难;
链表的特点是:寻址困难,插入和删除容易;
那么我们能不能综合两者的特性,做出一种寻址容易,插入删除也容易的数据结构?答案是肯定的,这就是我们要提起的哈希表
哈希表有多种不同的实现方法,我接下来解释的是最常用的一种方法—— ■拉链法,我们可以理解为“链表的数组”,如图:
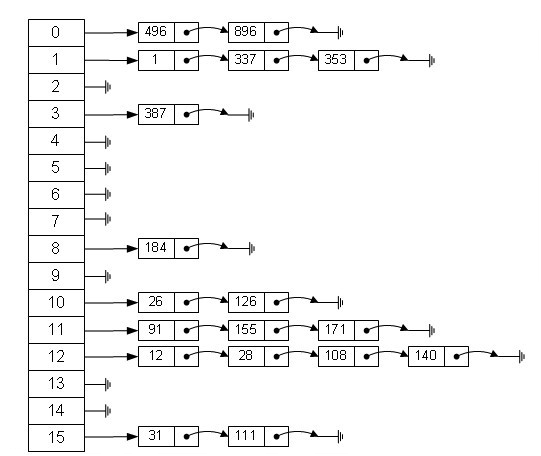
从上图我们可以发现哈希表是由数组+链表组成的,一个长度为16的数组中,■数组的每个元素存储的是一个链表的头结点。
元素存储到数组中的规则:
一般情况是通过hash(key)%len获得,也就是元素的key的哈希值对数组长度取模得到
比如上述哈希表中,12%16=12,28%16=12,108%16=12,140%16=12。所以12、28、108以及140都存储在数组下标为12的位置。
public interface Map<K, V> { // 【接口内部定义接口?】
void clear();
boolean containsKey(Object var1);
boolean containsValue(Object var1);
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet();
boolean equals(Object var1);
V get(Object var1);
int hashCode();
boolean isEmpty();
Set<K> keySet();
V put(K var1, V var2);
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> var1);
V remove(Object var1);
int size();
Collection<V> values();
public interface Entry<K, V> {
boolean equals(Object var1);
K getKey();
V getValue();
int hashCode();
V setValue(V var1);
}
}
HashMap的存取实现:
//存储时:
int hash = key.hashCode();// 这个hashCode方法这里不详述,只要理解每个key的hash是一个固定的int值
int index = hash % Entry[].length;
Entry[index] = value;
//取值时:
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash % Entry[].length;
return Entry[index];
HASH 冲突:
如果两个key通过hash%Entry[].length得到的index相同(也称为hash冲突),会不会有覆盖的危险?
只要key的 HashCode 相同才会覆盖旧值, hashCode%length 等于 index ,index相同那么会 插入到头结点后,形成新的LinkList结点。
https://blog.csdn.net/abcd1430/article/details/52745155
HashMap 采用一种所谓的“Hash 算法”来决定每个元素的存储位置。当程序执行 map.put(String,Obect)方法 时,
系统将调用String的 hashCode() 方法得到其 hashCode 值——每个 Java 对象都有 hashCode() 方法,
都可通过该方法获得它的 hashCode 值。
得到这个对象的 hashCode 值之后,系统会根据该 hashCode 值来决定该元素的存储位置。源码如下:
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); // 【获得Key的hash值 】
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//判断当前确定的索引位置是否存在相同hashcode和相同key的元素,如果存在相同的hashcode和相同的key的元素,那么新值覆盖原来的旧值,并返回旧值。
//如果存在相同的hashcode,那么他们确定的索引位置就相同,这时判断他们的key是否相同,如果不相同,这时就是产生了hash冲突。
//Hash冲突后,那么HashMap的单个bucket里存储的不是一个 Entry,而是一个 Entry 链。
//系统只能必须按顺序遍历每个 Entry,直到找到想搜索的 Entry 为止——如果恰好要搜索的 Entry 位于该 Entry 链的最末端(该 Entry 是最早放入该 bucket 中),
//那系统必须循环到最后才能找到该元素。
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
注:解决hash冲突的办法:
开放定址法(线性探测再散列,二次探测再散列,伪随机探测再散列)
再哈希法
链地址法 【Java 默认】
建立一个公共溢出区
HashMap的优化:
Entry[]的长度一定固定后,随着map里面数据的越来越长,这样同一个index的链就会很长,会不会影响性能?
HashMap里面设置一个因素(■也称为负载极限 负载因子),随着map的size越来越大,Entry[]会以一定的规则加长长度。
public HashMap(int capacity, float loadFactor) // HashMap 的构造器中设置 负载因子 loadFactor 默认 0.75
HashMap map = new HashMap(10, 0.8F);
//容量极限threshold=(int)(capacity*loadFacor); 当超过时就会增长一倍的长度resize(2*table.length);
HashMap默认的“负载极限”为0.75,表明该hash表3/4已经被填满时,hash表会发生rehashing
0.75其实是事件和空间的一个折中:
较高的“负载极限”可以降低hash表所占的内存空间,但会增加查询数据的开销,而查询是最频繁的操作;
而较低的“负载极限”会增加查询的性能,但会增加hash表所占的内存空间。
HashMap Hashtable SynchronizedMap和ConcurrentHashMap关系
HashMap、Hashtable、SynchronizedMap和ConcurrentHashMap关系
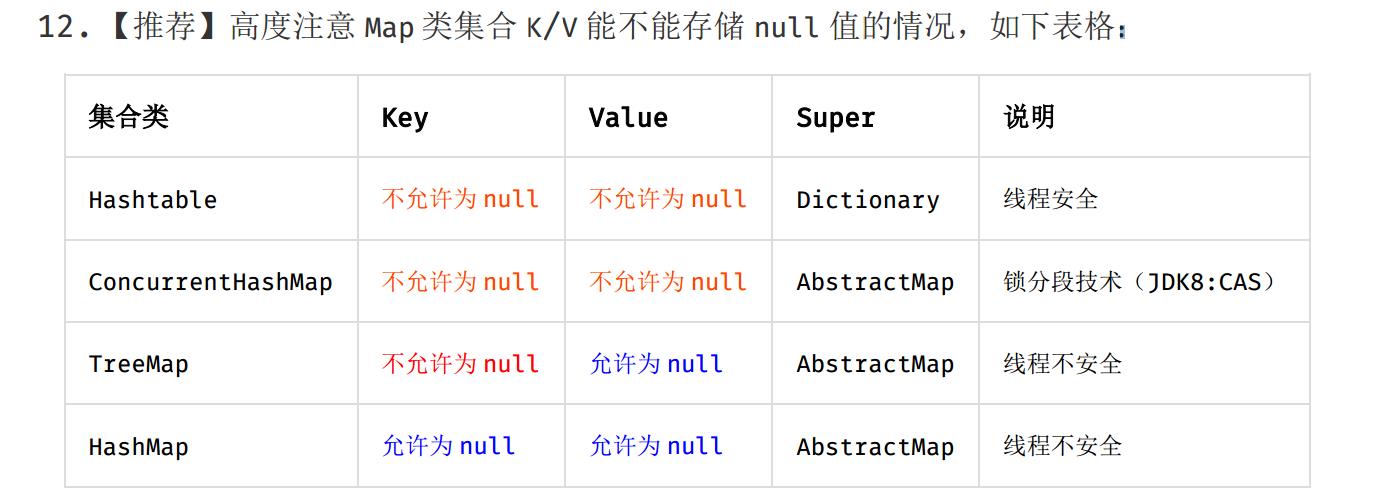
HashMap 与 Hashtable:
1. 不同点
一:
HashMap允许使用null作为key或者value,
Hashtable 不允许使用null 作为key 或者 value
二:
并且HashMap不是线程安全的 因为HashMap 定义的方法 都没有 synchronized 限制词修饰
Hashtable是线程安全的 因为Hashtable 定义的方法 全是 synchronized 限制词修饰
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put(null, null);
map.put("map_key", null);
map.put(null, "map_value"); // Key 相同 覆盖了上面的 map.put(null, null); 所以 Map的size为2
System.out.println(map.size());
Hashtable tab = new Hashtable();
tab.put(null, null); 【 往Hashtable 放空指针 会导致方法调用报错 】
tab.put("tab_key", null);
tab.put(null, "tab_value");
System.out.println(tab.size());
}
输出:
2
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at java.util.Hashtable.put(Unknown Source)
at test.MemoryCache.main(MemoryCache.java:17)
HashMap、Hashtable、SynchronizedMap和ConcurrentHashMap关系
HashMap不是线程安全的;
Hashtable线程安全,但效率低,因为是Hashtable是使用synchronized的,所有线程竞争同一把锁;
SynchronizedMap线程安全,其实是保持外部同步来实现的,效率也很低;
而ConcurrentHashMap不仅线程安全而且效率高,因为它包含一个segment数组,将数据分段存储,给每一段数据配一把锁,也就是所谓的锁分段技术。
如何线程安全的使用HashMap,无非就是以下三种方式:
Hashtable
Synchronized Map
ConcurrentHashMap
I
Integer 封装 int 的缓存问题
Integer A1= 100;
Integer A2= 100;
A1 == A2 【 TRUE 】
Integer B1= 200;
Integer B2= 200;
B1 == B2 【 FALSE 】
// 当直接赋值int 数据类型给 Integer 时 JAVA 会自动封装int 为 Integer类 同时缓存 -128 至 127 封装的对象
// 当下次创建时 需要JVM 封装相同的 int值 就不创建Integer 对象 而是直接 用原来的对象 来处理
public class Integet_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer A1= new Integer(11);
Integer A2= new Integer(11);
System.out.println(A1==A2?" A1 == A2":" A1! = A2");
Integer B1= new Integer(200);
Integer B2= new Integer(200);
System.out.println(B1==B2?" B1 == B2":" B1! = B2");
Integer C1= 0;
Integer C2= 0;
System.out.println(C1==C2?" C1 == C2":" C1! = C2");
Integer D1= -128;
Integer D2= -128;
System.out.println(D1==D2?" D1 == D2":" D1! = D2");
Integer E1= 127;
Integer E2= 127;
System.out.println(E1==E2?" E1 == E2":" E2! = E2");
Integer F1= 200;
Integer F2= 200;
System.out.println(F1==E2?" F1 == F2":" F1 != F2");
}
}
/*
* 输出:
*
A1! = A2
B1! = B2
C1 == C2
D1 == D2
E1 == E2
F1 != F2
*
*
*
* */
Interface接口中定义接口的问题(其实就是定义两个接口)
【接口内定义接口其实就是两个接口】
// 这个没有怎么回事,接口内定义接口其实就是两个接口。因为接口永远都是public的,
//只能说这样的写法风格不好。更好的写法是将两个接口单独使用两个类文件进行定义。
public interface InterfaceA {
void interfaceA_Method();
interface InterfaceA_ChildA {
void InterfaceA_ChildA_Method();
}
}
public class ObjectA implements InterfaceA.InterfaceA_ChildA{
@Override
public void InterfaceA_ChildA_Method() {
System.out.println("ObjectA [InterfaceA_ChildA_Method ] ");
}
public class ObjectA_ChildA implements InterfaceA{
@Override
public void interfaceA_Method() {
System.out.println("ObjectA_ChildA[ interfaceA_Method() ]");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectA_ChildA mObjectA_ChildA = (new ObjectA()). new ObjectA_ChildA(); //创建内部实例类
mObjectA_ChildA.interfaceA_Method();
ObjectA mObjectA = new ObjectA();
mObjectA.InterfaceA_ChildA_Method();
}
}
输出:
ObjectA_ChildA[ interfaceA_Method() ]
ObjectA [InterfaceA_ChildA_Method ]
Interface 允许多继承
Interface 接口允许多继承 , 如下 InterfaceABC 继承了 InterfaceA, InterfaceB, InterfaceC三个接口
public interface InterfaceExtendTest {
interface InterfaceA {}
interface InterfaceB {}
interface InterfaceC {}
interface InterfaceAB extends InterfaceA, InterfaceB {}
interface InterfaceABC extends InterfaceA, InterfaceB, InterfaceC {}
}
i++ 与 ++i 问题
package test;
public class NumPlusPlus {
int intA;
int intB;
int intC;
int intD;
static int[][] intArr = { { 1, 2, 3, 10 }, { 4, 5, 6, 100 }, { 7, 8, 9, 1000 } };
public static void main(String[] args) {
NumPlusPlus obj = new NumPlusPlus();
System.out.println("A++ A++ ([1][2])=" + intArr[obj.intA++][obj.intA++]);
System.out.println("B++ ++B ([1][3])= " + intArr[obj.intB++][++obj.intB]);
System.out.println("++C C++ ([2][2])= " + intArr[++obj.intC][obj.intC++]);
System.out.println("++D ++D ([2][3])= " + intArr[++obj.intD][++obj.intD]);
}
{
intA = 1;
intB = 1;
intC = 1;
intD = 1;
}
}
输出:
A++ A++ ([1][2])=6
B++ ++B ([1][3])= 100
++C C++ ([2][2])= 9
++D ++D ([2][3])= 1000
结论:
i++ 先赋值 再自增 原子性的 所以遇到的下一个 i必须是 增1的值
++i 先自增 再赋值 原子性的 所以遇到的下一个 i必须是 增1的值
IO流

IO流 Buffered【ByteOutput|ByteInput】Stream 以及Cipher DES加解密文件
 【为什么 解密之后的文件 与 原文件一样的字节bytes 但是所占用磁盘空间不一样呢?】
【为什么 解密之后的文件 与 原文件一样的字节bytes 但是所占用磁盘空间不一样呢?】
import java.io.*;
import java.security.Key;
import java.security.Security;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
public class B {
private static String strDefaultKey = "zukgit12"; // 加密原始秘钥字符串
/**
* ECB 作为DES加密 操作模式的一种 明文与密文长度一致 但必须保证8字节长度整数倍的明文
* CBC 作为DES加密 操作模式的一种 明文与密文长度不一致 明文长度不需要保证一定是 8字节整数倍 会多出一个 IV block padding
*/
private static Cipher encryptCipher = null;
private static Cipher decryptCipher = null;
static int BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH = 1024 * 10 * 10; // 读取文件Head字节数常数
static {
try {
/*
// 明文与密文大小不一致 明文大小可任意长度
// 明文 1 -------- 密文 8
// 明文 8 -------- 密文 16
// 明文 1024 -------- 密文 1032
Security.addProvider(new com.sun.crypto.provider.SunJCE());
Key key = getKey(strDefaultKey.getBytes());
encryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
encryptCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key);
decryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
decryptCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key);
*/
/* // 同默认的 DES 加密方式
Security.addProvider(new com.sun.crypto.provider.SunJCE());
Key key = getKey(strDefaultKey.getBytes());
IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(strDefaultKey.getBytes());
AlgorithmParameterSpec ap = iv;
encryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
encryptCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key, ap);
decryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
decryptCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key,ap);
*/
// 明文与密文大小一致 明文大小必须为8字节的整数倍 否则报错
// 报错类型为 javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException: Input length not multiple of 8 bytes
// 明文 8 -------- 密文 8
// 明文 16 -------- 密文 16
// 明文 1024 -------- 密文 1024
Security.addProvider(new com.sun.crypto.provider.SunJCE());
Key key = getKey(strDefaultKey.getBytes());
encryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/ECB/NoPadding");
encryptCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key);
decryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/ECB/NoPadding");
decryptCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
/**
* 从指定字符串生成密匙,密匙所需的字节数组度长为8位,缺乏8位时,面后补0,超越8位时,只取后面8位
*
* @param arrBTmp 成构字符串的字节数组
* @return 生成的密匙
*/
private static Key getKey(byte[] arrBTmp) throws Exception {
byte[] arrB = new byte[8]; //认默为0
for (int i = 0; i < arrBTmp.length && i < arrB.length; ++i) {
arrB[i] = arrBTmp[i];
}
//生成密匙
Key key = new javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec(arrB, "DES");
return key;
}
// 加密字节数组
public static byte[] encrypt(byte[] arrB) throws Exception {
return encryptCipher.doFinal(arrB);
}
//密解字节数组
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] arrB) throws Exception {
return decryptCipher.doFinal(arrB);
}
public static File generalFile;
public static File encryptFile;
public static File decryptFile;
public static byte[] TEMP = new byte[BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH];
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (isFileReady()) {
createEncryFile(); // 创建加密的文件
createDecryFile(); // 创建 解析 解密的文件之后的 解密的文件
show1024Byte();
}
}
public static boolean isFileReady() { // 初始化静态变量 File1 原始mp3文件 File2-加密mp3文件 File3-解密mp3文件
String usrDir = System.getProperties().getProperty("user.dir");
generalFile = new File(usrDir + File.separator + "1.mp3");
encryptFile = new File(usrDir + File.separator + "encrypt.mp3");
decryptFile = new File(usrDir + File.separator + "decryptFile.mp3");
if (!generalFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("原始文件 1.mp3 不存在,程序不能继续执行!");
return false;
}else{
System.out.println("存在原始文件 1.mp3,程序可以继续执行!");
}
if (!encryptFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("没有加密encrypt.mp3 文件,创建该文件");
try {
encryptFile.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建加密encrypt.mp3 成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.fillInStackTrace());
}
} else {
System.out.println("存在加密文件 encrypt.mp3 ");
}
if (!decryptFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("没有解密文件 创建解密文件 decryptFile.mp3");
try {
decryptFile.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建解密文件 decryptFile.mp3 成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.fillInStackTrace());
}
} else {
System.out.println("存在解密文件 decryptFile.mp3");
}
return true;
}
public static void createEncryFile() {
int general_position = 0;
int general_offset = 0;
FileInputStream generalFileInputStream = null;
BufferedInputStream generalBufferedInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream encryptileOutputStream = null;
BufferedOutputStream encryptBufferedOutputStream = null;
try {
generalFileInputStream = new FileInputStream(generalFile);
generalBufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(generalFileInputStream);
encryptileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(encryptFile);
encryptBufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(encryptileOutputStream);
System.out.println("原始文件字节大小: " + generalBufferedInputStream.available());
while (general_offset < BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH) { // 读取原始文件的头 BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH 个字节数进行加密
general_position = generalBufferedInputStream.read(TEMP, general_offset, TEMP.length - general_offset);
if (general_position == -1) {
break;
}
general_offset += general_position;
// byteTo16(TEMP, general_position); // 可以查看 指定 前 general_position 个在 TEMP数组中的字节数据 太多 注释掉
}
// 对读取到的TEMP字节数组 BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH 个字节进行 ECB模式加密 明文大小与密文大小一致
byte[] encrypt_bytes = encrypt(TEMP);
System.out.println("加密前明文大小:" + TEMP.length + " 加密后密文大小:" + encrypt_bytes.length);
//加密后的密文 填充 encryptFile文件的头首部
encryptBufferedOutputStream.write(encrypt_bytes, 0, encrypt_bytes.length);
encryptBufferedOutputStream.flush();
// 从正常的 general文件 读取 BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH 字节数之后的所有字节写入到 加密File(Head已经加密)文件中去
while ((general_position = generalBufferedInputStream.read(TEMP, 0, TEMP.length)) != -1) {
encryptBufferedOutputStream.write(TEMP, 0, general_position);
encryptBufferedOutputStream.flush();
}
// 关闭流
generalBufferedInputStream.close();
encryptBufferedOutputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.fillInStackTrace());
}
}
// 读取加密文件 对加密部分进行解密 然后生成解密之后的文件 decryptFile
public static void createDecryFile() {
FileOutputStream decryptileOutputStream = null;
BufferedOutputStream decryptBufferedOutputStream = null;
FileInputStream encryptileInputStream = null;
BufferedInputStream encryptBufferedInputStream = null;
try {
encryptileInputStream = new FileInputStream(encryptFile);
encryptBufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(encryptileInputStream);
decryptileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(decryptFile);
decryptBufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(decryptileOutputStream);
int encrypt_offset = 0;
int encrypt_position = 0;
while (encrypt_offset < BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH) { // 读取到加密文件的 加密字节部分 大小为 BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH
encrypt_position = encryptBufferedInputStream.read(TEMP, encrypt_offset, TEMP.length - encrypt_offset);
if (encrypt_position == -1) {
break;
}
encrypt_offset += encrypt_position;
// byteTo16(TEMP, general_position); // 可以查看 指定 前 general_position 个在 TEMP数组中的字节数据 太多 注释掉
}
byte[] decrypt_bytes = decrypt(TEMP); // 对加密文件的加密字节进行解密
System.out.println("密文加密字节大小:" + TEMP.length + " 解密密文之后的明文大小:" + decrypt_bytes.length);
decryptBufferedOutputStream.write(decrypt_bytes);
decryptBufferedOutputStream.flush();
// 读取 encryptFile加密文件中正常的字节 BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH 字节数之后的所有字节写入到 解密File(Head已经解密)文件中去
while ((encrypt_offset = encryptBufferedInputStream.read(TEMP, 0, TEMP.length)) != -1) {
decryptBufferedOutputStream.write(TEMP, 0, encrypt_offset);
decryptBufferedOutputStream.flush();
}
encryptBufferedInputStream.close();
decryptBufferedOutputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.fillInStackTrace());
}
}
public static void show1024Byte(){
FileInputStream generalFileInputStream = null;
BufferedInputStream generalBufferedInputStream = null;
FileInputStream encryptileInputStream = null;
BufferedInputStream encryptBufferedInputStream = null;
FileInputStream decryptileInputStream = null;
BufferedInputStream decryptBufferedInputStream = null;
try {
generalFileInputStream = new FileInputStream(generalFile);
generalBufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(generalFileInputStream);
encryptileInputStream = new FileInputStream(encryptFile);
encryptBufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(encryptileInputStream);
decryptileInputStream = new FileInputStream(decryptFile);
decryptBufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(decryptileInputStream);
int common_offset = 0;
int common_position = 0;
while (common_offset < BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH) { // 读取到加密文件的 加密字节部分 大小为 BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH
common_position = generalBufferedInputStream.read(TEMP, common_offset, TEMP.length - common_offset);
if (common_position == -1) {
break;
}
common_offset += common_position;
}
System.out.println("\n\n\n");
System.out.println("GeneralFile的前 1024 个字节的内容如下: ");
byteTo16(TEMP,1024);
common_offset = 0 ;
common_position = 0;
while (common_offset < BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH) { // 读取到加密文件的 加密字节部分 大小为 BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH
common_position = encryptBufferedInputStream.read(TEMP, common_offset, TEMP.length - common_offset);
if (common_position == -1) {
break;
}
common_offset += common_position;
}
System.out.println("\n\n\n");
System.out.println("encryptFile 加密文件的前 1024 个字节的内容如下: ");
byteTo16(TEMP,1024);
common_offset = 0 ;
common_position = 0;
while (common_offset < BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH) { // 读取到加密文件的 加密字节部分 大小为 BYTE_CONTENT_LENGTH
common_position = decryptBufferedInputStream.read(TEMP, common_offset, TEMP.length - common_offset);
if (common_position == -1) {
break;
}
common_offset += common_position;
}
System.out.println("\n\n\n");
System.out.println("decryptFile 解密文件的前 1024 个字节的内容如下: ");
byteTo16(TEMP,1024);
generalBufferedInputStream.close();
encryptBufferedInputStream.close();
decryptBufferedInputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static String byteTo16(byte bt) {
String[] strHex = {"0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"};
String resStr = "";
int low = (bt & 15);
int high = bt >> 4 & 15;
resStr = strHex[high] + strHex[low];
return resStr;
}
public static String byteTo16(byte[] btArr) {
String resStr = "";
int index = 0;
for (byte bt : btArr) {
String[] strHex = {"0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"};
int low = (bt & 15);
int high = bt >> 4 & 15;
resStr = strHex[high] + strHex[low];
if (index % 16 == 0) {
System.out.println();
//int numLine = index/16;
String pre = "";
if (index < 10) {
pre = "0000000000" + index;
} else if (index < 100) {
pre = "000000000" + index;
} else if (index < 1000) {
pre = "00000000" + index;
} else if (index < 10000) {
pre = "0000000" + index;
} else if (index < 100000) {
pre = "000000" + index;
} else if (index < 1000000) {
pre = "00000" + index;
} else if (index < 10000000) {
pre = "0000" + index;
} else if (index < 100000000) {
pre = "000" + index;
} else if (index < 1000000000) {
pre = "00" + index;
}
System.out.print(pre + "字节---" + toRightHexString(Integer.toHexString(index)) + "h :");
}
System.out.print(resStr + " ");
index++;
}
return resStr;
}
public static String byteTo16(byte[] btArr, int position) {
String resStr = "";
int index = 0;
for (byte bt : btArr) {
String[] strHex = {"0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"};
int low = (bt & 15);
int high = bt >> 4 & 15;
resStr = strHex[high] + strHex[low];
if (index % 16 == 0) {
System.out.println();
//int numLine = index/16;
String pre = "";
if (index < 10) {
pre = "0000000000" + index;
} else if (index < 100) {
pre = "000000000" + index;
} else if (index < 1000) {
pre = "00000000" + index;
} else if (index < 10000) {
pre = "0000000" + index;
} else if (index < 100000) {
pre = "000000" + index;
} else if (index < 1000000) {
pre = "00000" + index;
} else if (index < 10000000) {
pre = "0000" + index;
} else if (index < 100000000) {
pre = "000" + index;
} else if (index < 1000000000) {
pre = "00" + index;
}
System.out.print(pre + "字节---" + toRightHexString(Integer.toHexString(index)) + "h :");
}
System.out.print(resStr + " ");
index++;
if (index == position) {
break;
}
}
return resStr;
}
public static String toRightHexString(String hexStr) { // 以 00000 -- 99999 格式输出 字节 00000字节 --- 01008字节
if (hexStr.length() == 1) {
hexStr = "000000000" + hexStr;
} else if (hexStr.length() == 2) {
hexStr = "00000000" + hexStr;
} else if (hexStr.length() == 3) {
hexStr = "0000000" + hexStr;
} else if (hexStr.length() == 4) {
hexStr = "000000" + hexStr;
} else if (hexStr.length() == 5) {
hexStr = "00000" + hexStr;
} else if (hexStr.length() == 6) {
hexStr = "0000" + hexStr;
} else if (hexStr.length() == 7) {
hexStr = "000" + hexStr;
} else if (hexStr.length() == 8) {
hexStr = "00" + hexStr;
} else if (hexStr.length() == 9) {
hexStr = "0" + hexStr;
}
return hexStr;
}
}
输出结果:
存在原始文件 1.mp3,程序可以继续执行!
没有加密encrypt.mp3 文件,创建该文件
创建加密encrypt.mp3 成功
没有解密文件 创建解密文件 decryptFile.mp3
创建解密文件 decryptFile.mp3 成功
原始文件字节大小: 3431488
加密前明文大小:102400 加密后密文大小:102400
密文加密字节大小:102400 解密密文之后的明文大小:102400
GeneralFile的前 1024 个字节的内容如下:
00000000000字节---0000000000h :49 44 33 03 00 00 00 00 00 23 54 53 53 45 00 00
00000000016字节---0000000010h :00 0f 00 00 00 4c 61 76 66 35 37 2e 37 31 2e 31
00000000032字节---0000000020h :30 30 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff fb 90
00000000048字节---0000000030h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000064字节---0000000040h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000080字节---0000000050h :00 49 6e 66 6f 00 00 00 0f 00 00 20 11 00 34 5c
00000000096字节---0000000060h :13 00 03 06 08 0b 0d 0f 11 14 17 19 1c 1e 21 23
00000000112字节---0000000070h :26 28 2b 2e 30 33 35 38 3a 3d 40 42 45 47 4a 4c
00000000128字节---0000000080h :4f 51 54 57 59 5c 5e 61 63 66 68 6b 6e 70 73 75
00000000144字节---0000000090h :78 7a 7d 80 82 85 87 8a 8c 8f 91 94 97 99 9c 9e
00000000160字节---00000000a0h :a1 a3 a6 a8 ab ae b0 b3 b5 b8 ba bd c0 c2 c5 c7
00000000176字节---00000000b0h :ca cc cf d1 d4 d7 d9 dc de e1 e3 e6 e8 eb ee f0
00000000192字节---00000000c0h :f3 f5 f8 fa fd 00 00 00 00 4c 61 76 63 35 37 2e
00000000208字节---00000000d0h :38 39 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 24 04
00000000224字节---00000000e0h :80 00 00 00 00 00 34 5c 13 5d 89 2a 89 00 00 00
00000000240字节---00000000f0h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000256字节---0000000100h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000272字节---0000000110h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000288字节---0000000120h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000304字节---0000000130h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000320字节---0000000140h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000336字节---0000000150h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000352字节---0000000160h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000368字节---0000000170h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000384字节---0000000180h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000400字节---0000000190h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000416字节---00000001a0h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000432字节---00000001b0h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000448字节---00000001c0h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff fb
00000000464字节---00000001d0h :90 64 00 00 f3 0a 6d be c8 22 4f b0 00 00 0d 20
00000000480字节---00000001e0h :00 00 01 0d 11 b7 05 20 8d fe c0 00 00 34 80 00
00000000496字节---00000001f0h :00 04 9e 5e 07 fd 01 06 31 c6 ee 00 20 48 0b c6
00000000512字节---0000000200h :ff 02 00 01 8c 79 8f 18 01 82 05 cc 63 1b d4 81
00000000528字节---0000000210h :ff 9b ff ef d4 ee 46 7e 84 24 ed 39 ce 7c e2 08
00000000544字节---0000000220h :42 00 12 46 22 81 bb 1d f4 21 1a 8c b7 49 ff fd
00000000560字节---0000000230h :5e 42 37 ff ff ff ff ff f9 ed ef a8 20 63 f2 30
00000000576字节---0000000240h :db a6 ba 31 59 3d 42 cb 86 ca 1e 6c 04 03 00 10
00000000592字节---0000000250h :08 20 63 25 f9 b6 ae 00 07 b9 5c ce 96 72 9e 59
00000000608字节---0000000260h :73 53 ec bf 33 aa 84 c8 b2 dd 2f fe e2 e7 f9 19
00000000624字节---0000000270h :46 ce ba 33 c6 96 66 4a 84 bf 11 dc 42 77 72 1a
00000000640字节---0000000280h :a8 e0 20 83 58 0b d4 70 a1 f2 07 f0 fd b8 d3 22
00000000656字节---0000000290h :5d 16 d8 67 e6 8f fc fa ff 9d 7c 63 1f 7e de 17
00000000672字节---00000002a0h :ce f2 d6 f5 bd ec c8 17 fa 6f 66 3f 1c ae d8 e0
00000000688字节---00000002b0h :8c 35 8d ac 2d 8b ba b8 60 9c 55 9d ff ff ff b9
00000000704字节---00000002c0h :e7 a7 e7 2c 39 44 c6 5e 2b a6 63 02 7d 83 61 c1
00000000720字节---00000002d0h :8a a1 dd 82 03 1c 08 70 30 61 de 32 22 51 26 22
00000000736字节---00000002e0h :43 88 7c 3e 7c f7 cb b7 da e5 c0 87 bc ef 5a a7
00000000752字节---00000002f0h :be 3f af d4 38 72 c3 d5 28 f1 c1 b3 38 db c6 45
00000000768字节---0000000300h :ca 3c e5 4f 22 0d 03 08 eb 03 68 7e a8 42 a0 f0
00000000784字节---0000000310h :18 82 9a 47 1f 09 ba 65 ff a5 f9 4f ff ff ff ff
00000000800字节---0000000320h :ff ff ff df 23 d4 df 54 49 52 42 5f 25 11 c4 12
00000000816字节---0000000330h :21 48 c9 b0 ab c8 dc 1c 2d 13 3c c3 1e 63 46 43
00000000832字节---0000000340h :91 23 0d 88 45 3f 74 4a 66 fb 7c ad 77 f5 8f cc
00000000848字节---0000000350h :bd c9 8a 86 9e f9 de 6f 6d 7d ef 18 f0 6f 99 ed
00000000864字节---0000000360h :4b 28 df 5f a8 d6 e0 97 26 b9 98 9a d6 d3 23 ff
00000000880字节---0000000370h :fb 92 64 59 8f f2 d9 6d c0 00 03 7f 40 00 00 0d
00000000896字节---0000000380h :20 00 00 01 0d 61 b6 fe 00 99 fe c0 00 00 34 80
00000000912字节---0000000390h :00 00 04 91 2e 3e 17 48 c0 7c 8e 71 0e 6c 04 6c
00000000928字节---00000003a0h :45 81 58 3b 12 b3 aa 4c 41 4d 45 33 2e 39 39 2e
00000000944字节---00000003b0h :35 aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa
00000000960字节---00000003c0h :aa aa aa aa e5 ff f9 57 ff ff ff ff ff ff ff 4f
00000000976字节---00000003d0h :8f 9f 3c 7c 32 bd 66 4f bc da 3d 29 51 34 a4 cd
00000000992字节---00000003e0h :df a0 25 bb 58 b4 a0 f9 82 39 11 32 04 d8 7d fa
00000001008字节---00000003f0h :2d 78 f8 dd df 7b f7 ff 2f c4 d6 55 f7 5c 63 65
encryptFile 加密文件的前 1024 个字节的内容如下:
00000000000字节---0000000000h :bb d9 27 9e 34 ba 19 0f 91 df 9a 30 58 62 54 e3
00000000016字节---0000000010h :e7 3b 66 d4 95 87 4c 43 62 f7 b8 b6 f0 d2 c5 91
00000000032字节---0000000020h :b4 7f be bf f2 cb da 28 2c c5 de af de be 3c 62
00000000048字节---0000000030h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000064字节---0000000040h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000080字节---0000000050h :d9 0a da fd 67 6b 7f a0 53 55 09 17 bf 6f d5 a5
00000000096字节---0000000060h :16 81 44 45 f8 12 27 46 56 6f 1a 61 73 dd 7f 7a
00000000112字节---0000000070h :93 b4 5d 92 49 b4 6d df e8 02 c8 ed 51 e1 3c 2b
00000000128字节---0000000080h :bf 67 94 4b d0 6c e1 53 d4 84 15 aa c9 83 7f 5b
00000000144字节---0000000090h :36 14 e2 84 c7 e6 bf 80 70 d6 00 15 d7 05 85 9d
00000000160字节---00000000a0h :a8 85 74 53 39 92 cf 38 d5 2c b0 7e 8a 56 38 dd
00000000176字节---00000000b0h :f0 d5 45 9c 6e 4b c8 06 a3 9b 79 4c 8c 49 29 6c
00000000192字节---00000000c0h :0f 02 cb 69 cb 8f 8c 6c 06 ff 13 7c 4c 65 25 15
00000000208字节---00000000d0h :82 95 09 9a 56 70 77 ed 0e 54 1a 45 e0 78 0f 11
00000000224字节---00000000e0h :b5 9d 16 56 ab 0f 00 6d 00 c2 ff c0 93 8f 57 58
00000000240字节---00000000f0h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000256字节---0000000100h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000272字节---0000000110h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000288字节---0000000120h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000304字节---0000000130h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000320字节---0000000140h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000336字节---0000000150h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000352字节---0000000160h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000368字节---0000000170h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000384字节---0000000180h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000400字节---0000000190h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000416字节---00000001a0h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000432字节---00000001b0h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85
00000000448字节---00000001c0h :86 75 63 bd dc f8 9b 85 e1 d8 74 08 ff 7a 23 5a
00000000464字节---00000001d0h :ec d1 15 6a 60 46 10 55 b2 29 6b 2e 79 d7 d7 64
00000000480字节---00000001e0h :59 84 f8 63 8c 32 e7 1a ba d1 74 bc 3b 81 30 26
00000000496字节---00000001f0h :72 d5 cd ca 4b 8a ea 16 c9 90 09 09 22 b0 7c 5e
00000000512字节---0000000200h :7d 8f 1d 40 74 e1 b5 48 73 c1 0b 22 19 57 d8 4b
00000000528字节---0000000210h :7f 57 4c fc b7 d1 b9 de 5e a9 dd c1 38 b1 74 30
00000000544字节---0000000220h :2a 2d 84 8c 35 54 15 04 42 e0 b5 11 2e 26 a6 c2
00000000560字节---0000000230h :25 d4 f3 19 bc 1c 62 59 f3 02 71 d4 15 a1 09 da
00000000576字节---0000000240h :de 40 36 cb 75 6e db fa bb 66 a2 e8 fc cd 49 fc
00000000592字节---0000000250h :66 1e b0 92 19 12 15 d3 d7 d3 c6 26 af 41 a5 d7
00000000608字节---0000000260h :10 20 94 35 8d e8 83 69 52 cd b5 f5 b1 db 3c 5c
00000000624字节---0000000270h :83 37 5d b3 48 86 ff 44 36 16 06 2e 48 7e 9d ef
00000000640字节---0000000280h :22 25 9b df 7d 50 a6 53 fd 88 bc 8b 42 02 4a 8a
00000000656字节---0000000290h :7e 5c 10 d3 a1 f7 51 2d ad 51 8a a4 77 65 ef 7d
00000000672字节---00000002a0h :28 f0 1c c1 04 eb 61 83 c1 16 af cf 77 c5 1b ee
00000000688字节---00000002b0h :f7 94 80 64 87 f0 f3 e9 08 c7 7c 49 68 c7 08 45
00000000704字节---00000002c0h :a9 03 08 35 1e 6f 92 f2 50 d8 bf 04 7c ea c0 4a
00000000720字节---00000002d0h :0d b7 c5 9e 57 0c df 55 e6 89 be d2 82 b4 9e 14
00000000736字节---00000002e0h :6f 27 00 72 25 3e ff bb 44 33 c4 35 2d b1 b8 69
00000000752字节---00000002f0h :14 0b 38 7d c9 d4 a7 6d 2a 0f 5d b2 e1 d3 92 ea
00000000768字节---0000000300h :94 ef 8c dc 7c 96 e8 46 b9 f3 ef 1f 96 48 4f 36
00000000784字节---0000000310h :20 ce 8d ad 75 37 67 ac a1 99 a3 0d 48 6c 30 b4
00000000800字节---0000000320h :2e 4a b8 26 ed bb 2b 98 60 39 bc 80 77 2b 9f 89
00000000816字节---0000000330h :db a7 8e bb 9e 1c 2e 38 9f 23 9f 0b b7 14 92 99
00000000832字节---0000000340h :fb de 20 43 67 f6 21 3c 72 ae ce 94 b7 b9 a8 13
00000000848字节---0000000350h :b6 23 06 5d e7 e4 22 f7 40 91 c2 fa 1d 81 18 f5
00000000864字节---0000000360h :69 bb 22 8b 8e f8 2c 9e d4 f1 13 83 41 57 b5 07
00000000880字节---0000000370h :5a f2 b4 e1 b5 63 e3 4e c6 1e 35 8b 28 2f 6b 94
00000000896字节---0000000380h :64 49 6a 3e ed f1 60 55 a4 da c3 68 f8 a6 18 17
00000000912字节---0000000390h :e9 26 5f 1b 80 80 86 d5 d1 aa 41 d0 1e 54 a4 45
00000000928字节---00000003a0h :53 76 e6 97 ef c7 e4 1a ce 38 e0 6d 27 f4 37 dd
00000000944字节---00000003b0h :62 34 d4 ca db 74 b4 d8 c9 68 b3 0b f1 be 80 4e
00000000960字节---00000003c0h :d3 98 23 e9 0c 4a 15 d8 49 b5 22 b2 c2 ba 33 14
00000000976字节---00000003d0h :8e 8a 23 80 dd 8c 9d 7f c5 3f f1 7d ec 69 a9 0b
00000000992字节---00000003e0h :0d 1c 9b 04 1e 04 8d b6 de ec 4c 94 33 4c 15 6c
00000001008字节---00000003f0h :7e 94 93 c2 0e bb b7 07 7f e9 dc 17 09 06 48 08
decryptFile 解密文件的前 1024 个字节的内容如下:
00000000000字节---0000000000h :49 44 33 03 00 00 00 00 00 23 54 53 53 45 00 00
00000000016字节---0000000010h :00 0f 00 00 00 4c 61 76 66 35 37 2e 37 31 2e 31
00000000032字节---0000000020h :30 30 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff fb 90
00000000048字节---0000000030h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000064字节---0000000040h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000080字节---0000000050h :00 49 6e 66 6f 00 00 00 0f 00 00 20 11 00 34 5c
00000000096字节---0000000060h :13 00 03 06 08 0b 0d 0f 11 14 17 19 1c 1e 21 23
00000000112字节---0000000070h :26 28 2b 2e 30 33 35 38 3a 3d 40 42 45 47 4a 4c
00000000128字节---0000000080h :4f 51 54 57 59 5c 5e 61 63 66 68 6b 6e 70 73 75
00000000144字节---0000000090h :78 7a 7d 80 82 85 87 8a 8c 8f 91 94 97 99 9c 9e
00000000160字节---00000000a0h :a1 a3 a6 a8 ab ae b0 b3 b5 b8 ba bd c0 c2 c5 c7
00000000176字节---00000000b0h :ca cc cf d1 d4 d7 d9 dc de e1 e3 e6 e8 eb ee f0
00000000192字节---00000000c0h :f3 f5 f8 fa fd 00 00 00 00 4c 61 76 63 35 37 2e
00000000208字节---00000000d0h :38 39 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 24 04
00000000224字节---00000000e0h :80 00 00 00 00 00 34 5c 13 5d 89 2a 89 00 00 00
00000000240字节---00000000f0h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000256字节---0000000100h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000272字节---0000000110h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000288字节---0000000120h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000304字节---0000000130h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000320字节---0000000140h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000336字节---0000000150h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000352字节---0000000160h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000368字节---0000000170h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000384字节---0000000180h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000400字节---0000000190h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000416字节---00000001a0h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000432字节---00000001b0h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000000448字节---00000001c0h :00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff fb
00000000464字节---00000001d0h :90 64 00 00 f3 0a 6d be c8 22 4f b0 00 00 0d 20
00000000480字节---00000001e0h :00 00 01 0d 11 b7 05 20 8d fe c0 00 00 34 80 00
00000000496字节---00000001f0h :00 04 9e 5e 07 fd 01 06 31 c6 ee 00 20 48 0b c6
00000000512字节---0000000200h :ff 02 00 01 8c 79 8f 18 01 82 05 cc 63 1b d4 81
00000000528字节---0000000210h :ff 9b ff ef d4 ee 46 7e 84 24 ed 39 ce 7c e2 08
00000000544字节---0000000220h :42 00 12 46 22 81 bb 1d f4 21 1a 8c b7 49 ff fd
00000000560字节---0000000230h :5e 42 37 ff ff ff ff ff f9 ed ef a8 20 63 f2 30
00000000576字节---0000000240h :db a6 ba 31 59 3d 42 cb 86 ca 1e 6c 04 03 00 10
00000000592字节---0000000250h :08 20 63 25 f9 b6 ae 00 07 b9 5c ce 96 72 9e 59
00000000608字节---0000000260h :73 53 ec bf 33 aa 84 c8 b2 dd 2f fe e2 e7 f9 19
00000000624字节---0000000270h :46 ce ba 33 c6 96 66 4a 84 bf 11 dc 42 77 72 1a
00000000640字节---0000000280h :a8 e0 20 83 58 0b d4 70 a1 f2 07 f0 fd b8 d3 22
00000000656字节---0000000290h :5d 16 d8 67 e6 8f fc fa ff 9d 7c 63 1f 7e de 17
00000000672字节---00000002a0h :ce f2 d6 f5 bd ec c8 17 fa 6f 66 3f 1c ae d8 e0
00000000688字节---00000002b0h :8c 35 8d ac 2d 8b ba b8 60 9c 55 9d ff ff ff b9
00000000704字节---00000002c0h :e7 a7 e7 2c 39 44 c6 5e 2b a6 63 02 7d 83 61 c1
00000000720字节---00000002d0h :8a a1 dd 82 03 1c 08 70 30 61 de 32 22 51 26 22
00000000736字节---00000002e0h :43 88 7c 3e 7c f7 cb b7 da e5 c0 87 bc ef 5a a7
00000000752字节---00000002f0h :be 3f af d4 38 72 c3 d5 28 f1 c1 b3 38 db c6 45
00000000768字节---0000000300h :ca 3c e5 4f 22 0d 03 08 eb 03 68 7e a8 42 a0 f0
00000000784字节---0000000310h :18 82 9a 47 1f 09 ba 65 ff a5 f9 4f ff ff ff ff
00000000800字节---0000000320h :ff ff ff df 23 d4 df 54 49 52 42 5f 25 11 c4 12
00000000816字节---0000000330h :21 48 c9 b0 ab c8 dc 1c 2d 13 3c c3 1e 63 46 43
00000000832字节---0000000340h :91 23 0d 88 45 3f 74 4a 66 fb 7c ad 77 f5 8f cc
00000000848字节---0000000350h :bd c9 8a 86 9e f9 de 6f 6d 7d ef 18 f0 6f 99 ed
00000000864字节---0000000360h :4b 28 df 5f a8 d6 e0 97 26 b9 98 9a d6 d3 23 ff
00000000880字节---0000000370h :fb 92 64 59 8f f2 d9 6d c0 00 03 7f 40 00 00 0d
00000000896字节---0000000380h :20 00 00 01 0d 61 b6 fe 00 99 fe c0 00 00 34 80
00000000912字节---0000000390h :00 00 04 91 2e 3e 17 48 c0 7c 8e 71 0e 6c 04 6c
00000000928字节---00000003a0h :45 81 58 3b 12 b3 aa 4c 41 4d 45 33 2e 39 39 2e
00000000944字节---00000003b0h :35 aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa
00000000960字节---00000003c0h :aa aa aa aa e5 ff f9 57 ff ff ff ff ff ff ff 4f
00000000976字节---00000003d0h :8f 9f 3c 7c 32 bd 66 4f bc da 3d 29 51 34 a4 cd
00000000992字节---00000003e0h :df a0 25 bb 58 b4 a0 f9 82 39 11 32 04 d8 7d fa
00000001008字节---00000003f0h :2d 78 f8 dd df 7b f7 ff 2f c4 d6 55 f7 5c 63 65
IO流 字符流 执行读取文件字符串并指定规则进行排序
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class A {
public static final int NUM_ERERY_LINE_OLD = 9; // 输入1.txt文件原本的每行列数 限制条件为 NEW/OLD 是正整数
public static final int NUM_ERERY_LINE_NEW = 9; // 输出2.txt 文件需要自定义的产生的每行列数
public static final int PADDING_COLOM = 5; // 填充padding的距离 每个列之间的间距
public static final boolean NEED_SORT = false; // 输出是否需要进行A-Z的排序 默认为false 默认为按照1.txt的读取顺序显示
public static final boolean DEBUG_LOG = false; // 是否打印Log标识
public static final String SRC_FILE_NAME = "1.txt"; // 输入文件1.txt
public static final String DES_FILE_NAME = "2.txt"; // 输出文件1.txt
public static String[] splitArr; // 读取输入 1.txt每行 原始的split返回值字符串数组
public static String[] retContentArr; // 读取输入 1.txt每行 原始的split返回值经过过滤规格过滤后的返回值字符串数组
public static long fileSumLines; // 输入文件1.txt 的总行数
public static long newSumLines; // 输出文件 2.txt 的总行数
public static long stringNumOfInput_Max; // 输入和输出文件中字符串的最大的个数
public static int[] item_Max_Length = new int[NUM_ERERY_LINE_NEW]; // 在1.txt输入文件每个列中字符串的最大长度的数组 默认为0
public static int[] item_Max_Length_new = new int[NUM_ERERY_LINE_NEW]; // 在2.txt文件中每个列的字符串最大长度 不足的补充padding
public static void main(String[] args) {
getLineNum(); // 获得当前输入的数据统计
try {
//链表数组 包含的是上面 LinkedList<String[]> 中的每一个String,这些String已经排序排好了
LinkedList<String> sortStringlist = getAllStringItemFromInput();
// 依据标识位 对 所有的String 进行排序
sortStringlist = sortAllStringItemMethod(sortStringlist);
// 链表数组 成员都是 每一行字符串进行split分割后产生的字符串数组 并且每个Item 对应的String[] 长度是 NUM_ERERY_LINE_NEW
LinkedList<String[]> list_StringArr = new LinkedList<String[]>();
// 填充输入到2.txt中的字符串数组的List
fill_List_StringArr(list_StringArr, sortStringlist);
// list_StringArr.length 就是 2.txt输出文件的行数
System.out.println("list_StringArr.length 输出文件2.txt 总行数:" + list_StringArr.size());
//int[] item_Max_Length 数组进行查找 找到每列最大的字符串长度
getStringMaxLengthMethod(list_StringArr);
// 创建2.txt 并填充数据
fillOutputFile(list_StringArr);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.fillInStackTrace());
}
}
public static void fill_List_StringArr(LinkedList<String[]> list_StringArr, LinkedList<String> sortStringlist) {
String[] newRow = new String[NUM_ERERY_LINE_NEW];
for (int i = 0; i < sortStringlist.size(); i++) {
int index = i % NUM_ERERY_LINE_NEW;
if (index == 0 && i > 0) {
list_StringArr.add(newRow);
newRow = new String[NUM_ERERY_LINE_NEW];
}
newRow[index] = sortStringlist.get(i);
}
if (!list_StringArr.contains(newRow)) {
list_StringArr.add(newRow);
}
}
// 对 list_StringArr 内容进行重新填充 到 LinkedList<String[]> list_StringArr
public static void fixSortInStringArrList(LinkedList<String[]> list_StringArr, LinkedList<String> sortStringlist) {
int num = 0;
for (String[] item : list_StringArr) {
for (int i = 0; i < item.length; i++) {
if (num + i < sortStringlist.size()) {
item[i] = sortStringlist.get(num + i);
}
}
num = num + item.length;
}
}
public static String[] getStringArr_From_EveryRow(String contentString, int num) {
retContentArr = new String[num];
if (contentString != null && !"".equals(contentString)) {
if (num == 1) {
splitArr = contentString.split(" ");
splitArr = makeEmptyOut(splitArr); // 把数组中的空字符 完全剔除
if (splitArr.length > num) {
String contentLine = splitArr[0];
String fixString = fixStringMethod(contentLine);
retContentArr[0] = fixString;
if (DEBUG_LOG) System.out.println("只读取每行第一个字符串 = "+splitArr[0]);
}
}
if (num == 2) {
splitArr = contentString.split(" ");
splitArr = makeEmptyOut(splitArr); // 把数组中的空字符 完全剔除
if (splitArr.length > num) {
retContentArr[0] = splitArr[0];
retContentArr[1] = splitArr[splitArr.length - 1];
} else if (splitArr.length == num) {
retContentArr[0] = splitArr[0];
retContentArr[1] = splitArr[1];
}
} else {
splitArr = contentString.split(" ");
if (DEBUG_LOG) System.out.println("行数大于等于3: 值为“+ num+ ” 切割长度为 splitArr.length =" + splitArr.length);
splitArr = makeEmptyOut(splitArr); // 把数组中的空字符 完全剔除
for (int x = 0; x < splitArr.length; x++) {
if (DEBUG_LOG) System.out.println("index =" + x + " content:" + splitArr[x]);
if (x == splitArr.length - 1) {
if (DEBUG_LOG) System.out.println();
}
}
if (splitArr.length > num) {
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {
retContentArr[i] = splitArr[i];
}
} else if (splitArr.length == num) {
for (int x = 0; x < splitArr.length; x++) {
retContentArr[x] = splitArr[x];
}
}
}
}
if (DEBUG_LOG) {
for (String value : retContentArr) {
System.out.println("value = " + value);
}
}
return retContentArr;
}
public static String fixStringMethod(String contentString) {
int length = contentString.length();
// System.out.println("contentString1"+ contentString);
if (contentString.contains(" ")) {
contentString = contentString.split(" ")[0].trim();
} else if (contentString.contains("\t")) {
contentString = contentString.split("\t")[0].trim();
}
System.out.println("contentString2 = " + contentString);
return contentString;
}
public static String[] makeEmptyOut(String[] strArr) {
String[] validStrArrRet = null;
ArrayList<String> validStrArr = new ArrayList<String>();
if (strArr != null) {
for (String strItem : strArr) {
if (strItem == null || "".equals(strItem.trim())) {
continue;
}
validStrArr.add(strItem);
}
}
if (validStrArr.size() > 0) {
validStrArrRet = new String[validStrArr.size()];
for (int x = 0 ; x < validStrArr.size(); x++) {
validStrArrRet[x] = validStrArr.get(x).trim();
}
}
return validStrArrRet;
}
public static boolean isArrEmpty(String[] strArr) {
boolean flag = false;
if (strArr != null) {
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < strArr.length; i++) {
if (strArr[i] != null && "".equals(strArr[i])) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
} else {
flag = true;
}
return flag;
}
public static boolean checkInsert(int i, int j) {
boolean flag = false;
if (retContentArr != null && splitArr != null && i < retContentArr.length && j < splitArr.length) {
if ("".equals(retContentArr[i]) && !"".equals(splitArr[j])) {
flag = true;
}
}
return flag;
}
public static LinkedList<String> getAllStringItemFromInput() {
//链表数组 包含的是上面 LinkedList<String[]> 中的每一个String,这些String已经排序排好了
LinkedList<String> sortStringlist = new LinkedList<String>();
try {
File txtFile = new File(System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator + SRC_FILE_NAME);
FileReader txtReader = new FileReader(txtFile);
BufferedReader txtBR = new BufferedReader(txtReader);
String lineContentFirst = ""; // 读取到的输入文件 1.txt 的每一行字符串
// 一次性读出所有的字符串String 然后再重新编排?
while (lineContentFirst != null) {
lineContentFirst = txtBR.readLine(); // 从1.txt中读取一行字符串出来
if (lineContentFirst == null) { // 如果读取到的字符串为null 说明读取到了末尾了
System.out.println("1.txt read to end!");
break;
}
// 对读取到的每行字符串 进行分拆 得到每一个当前字符串分拆后的数组
String[] arrStr = getStringArr_From_EveryRow(lineContentFirst, NUM_ERERY_LINE_OLD);
if (arrStr != null && arrStr.length == NUM_ERERY_LINE_OLD) {
for (String strItem : arrStr) {
sortStringlist.add(strItem); // 包含了所有切分出来的字符串
}
}
}
txtBR.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.fillInStackTrace());
}
return sortStringlist;
}
public static LinkedList<String> sortAllStringItemMethod(LinkedList<String> sortStringlist) {
// sortStringlist.size() 是 2.txt 输出中所有字符串的数量
System.out.println("sortStringlist.length :" + sortStringlist.size());
if (NEED_SORT) {
sortStringlist.sort(new Comparator<String>() { // 对字符串进行排序使得 aA-zZ这样的排序
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
return o1.toLowerCase().compareTo(o2.toLowerCase());
}
});
}
// 打印排序后的字符串
if (DEBUG_LOG) {
for (String sortItem : sortStringlist) {
System.out.println("sortItem:" + sortItem);
}
}
return sortStringlist;
}
public static void getLineNum() {
try {
File txtFile = new File(System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator + SRC_FILE_NAME);
FileReader txtReader = new FileReader(txtFile);
BufferedReader txtBR = new BufferedReader(txtReader);
fileSumLines = txtBR.lines().count(); // 当前输入 1.txt的行数
// 当前输入 1.txt 所包含该的String字符串最大的数量 也是输入文件2.txt最大的字符串数量
stringNumOfInput_Max = fileSumLines * NUM_ERERY_LINE_OLD;
newSumLines = (stringNumOfInput_Max / NUM_ERERY_LINE_NEW) +1;
System.out.println("old_txt_lines=" + fileSumLines + " newSumLines=" + newSumLines + " AllStringNum = " + stringNumOfInput_Max);
txtBR.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.fillInStackTrace());
}
}
public static void getStringMaxLengthMethod(LinkedList<String[]> list_StringArr) {
if (list_StringArr != null) {
int num = 0;
for (String[] item : list_StringArr) { // 计算出每列的最长的字符串的长度
if (item == null) {
if (DEBUG_LOG) System.out.println("item == null");
continue;
}
// System.out.println("item != null index:"+ (num++) +"item.length="+item.length);
for (int z = 0; z < item.length; z++) {
if (item[z] == null) {
if (DEBUG_LOG) System.out.println("item[z] = null");
continue;
}
if (item[z] != null && item[z].length() > item_Max_Length[z]) {
if (DEBUG_LOG) System.out.println("item[z].length() = " + item[z].length());
item_Max_Length[z] = item[z].length();
}
}
}
// 设置2.txt的每一列的长度值
for (int itemContentLength = 0; itemContentLength < item_Max_Length.length; itemContentLength++) {
item_Max_Length_new[itemContentLength] = item_Max_Length[itemContentLength] + PADDING_COLOM; // 每一列的长度值最长值+1 避免内容重叠
if (DEBUG_LOG)
System.out.println("item_Max_Length_new_index:" + itemContentLength + " item_Max_Length_new_value:" + item_Max_Length_new[itemContentLength]);
}
}
}
public static void fillOutputFile(LinkedList<String[]> list_StringArr) {
try {
File txt2File = new File(System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator + DES_FILE_NAME);
if (!txt2File.exists()) {
txt2File.createNewFile();
}
FileWriter txt2Writer = new FileWriter(txt2File);
BufferedWriter txt2BW = new BufferedWriter(txt2Writer);
//2.txt的内容进行填充 list_StringArr 中 每一个String【] 是 2.txt 中的一行】
for (String[] item : list_StringArr) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("");
if (item == null) {
if (DEBUG_LOG) System.out.println("item == null");
continue;
}
if (DEBUG_LOG) {
System.out.println("item != null item.length=" + item.length);
int index = 0;
for (String str : item) {
System.out.println("item[" + index + "] != null " + "item[" + index + "]" + str);
index++;
}
}
for (int z = 0; z < item.length; z++) {
if (item[z] == null) {
continue;
}
int padding = item_Max_Length_new[z] - item[z].length();
String paddingStr = "";
for (int paddingNum = 0; paddingNum < padding; paddingNum++) {
paddingStr += " ";
}
String content = item[z] + paddingStr;
sb.append(content);
}
txt2BW.write(sb.toString());
txt2BW.newLine();
}
txt2BW.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.fillInStackTrace());
}
}
}
输出Log:
old_txt_lines=16 newSumLines=17 AllStringNum = 144
1.txt read to end!
sortStringlist.length :144
list_StringArr.length 输出文件2.txt 总行数:16
输入文件: 1.txt
drwx------@ 71 aaa staff 2414 8 5 12:26 Library
drwx------+ 3 aaa staff 102 3 20 2017 Movies
drwx------+ 5 aaa staff 170 7 22 2017 Music
drwx------+ 5 aaa staff 170 5 29 2017 Pictures
drwxr-xr-x+ 5 aaa staff 170 3 20 2017 Public
-rw-r--r-- 1 aaa staff 44578168 8 14 19:44 QQ
-rw-r--r-- 1 aaa staff 64 8 14 19:44 QQ.aria2
drwxr-xr-x 4 aaa staff 136 9 2 2017 VirtualBox
-rw-r--r-- 1 aaa staff 489 8 14 11:14 antigen-shapshot
-rw-r--r-- 1 root staff 19224072 8 13 15:13 finalshell_data.zip
-rwxr-xr-x 1 aaa staff 3572 8 13 15:13 finalshell_install.sh
drwxr-xr-x 4 aaa staff 136 10 25 2017 git_space
-rw-r--r--@ 1 aaa staff 76016 8 25 2017 screen.png
drwxr-xr-x 2 aaa staff 68 5 15 2017 soft_work
drwxr-xr-x 4 aaa staff 136 9 2 2017 镜像
-rw-r--r--@ 1 aaa staff 188521 2 6 2018 坊头.dwg
输出文件: 2.txt
drwx------@ 71 aaa staff 2414 8 5 12:26 Library
drwx------+ 3 aaa staff 102 3 20 2017 Movies
drwx------+ 5 aaa staff 170 7 22 2017 Music
drwx------+ 5 aaa staff 170 5 29 2017 Pictures
drwxr-xr-x+ 5 aaa staff 170 3 20 2017 Public
-rw-r--r-- 1 aaa staff 44578168 8 14 19:44 QQ
-rw-r--r-- 1 aaa staff 64 8 14 19:44 QQ.aria2
drwxr-xr-x 4 aaa staff 136 9 2 2017 VirtualBox
-rw-r--r-- 1 aaa staff 489 8 14 11:14 antigen-shapshot
-rw-r--r-- 1 root staff 19224072 8 13 15:13 finalshell_data.zip
-rwxr-xr-x 1 aaa staff 3572 8 13 15:13 finalshell_install.sh
drwxr-xr-x 4 aaa staff 136 10 25 2017 git_space
-rw-r--r--@ 1 aaa staff 76016 8 25 2017 screen.png
drwxr-xr-x 2 aaa staff 68 5 15 2017 soft_work
drwxr-xr-x 4 aaa staff 136 9 2 2017 镜像
-rw-r--r--@ 1 aaa staff 188521 2 6 2018 坊头.dwg
IO流 把两个txt文件按行数顺序拼合到一个文件中、
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Pattern {
public static final String A_File = "1.txt"; // 输入文件1.txt
public static final String B_File = "2.txt"; // 输出文件1.txt
public static final String AB_File = "out.txt"; // 输出文件1.txt
public static void main(String[] args) {
File txtFile = new File(System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator+"/src/" + A_File);
File txtFileB = new File(System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator+"/src/" + B_File);
File txtFileOut = new File(System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator+"/src/" + AB_File);
if(!txtFileOut.exists()){
try {
txtFileOut.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
FileReader txtReader;
FileReader txtReaderB;
FileWriter txtWriter ;
try {
txtReader = new FileReader(txtFile);
txtReaderB = new FileReader(txtFileB);
txtWriter = new FileWriter(txtFileOut);
BufferedReader txtBR_A = new BufferedReader(txtReader);
BufferedReader txtBR_B = new BufferedReader(txtReaderB);
BufferedWriter txtBW_AB = new BufferedWriter(txtWriter);
String lineContentFirst_A = ""; // 读取到的输入文件 1.txt 的每一行字符串
String lineContentFirst_B = ""; // 读取到的输入文件 1.txt 的每一行字符串
// 一次性读出所有的字符串String 然后再重新编排?
while (lineContentFirst_A != null && lineContentFirst_B != null) {
lineContentFirst_A = txtBR_A.readLine(); // 从1.txt中读取一行字符串出来
lineContentFirst_B = txtBR_B.readLine(); // 从1.txt中读取一行字符串出来
if (lineContentFirst_A == null || lineContentFirst_B == null ) { // 如果读取到的字符串为null 说明读取到了末尾了
System.out.println("1.txt read to end!");
txtBW_AB.flush();
break;
}
String newLineStr = lineContentFirst_A +" "+ lineContentFirst_B;
txtBW_AB.write(newLineStr);
txtBW_AB.newLine();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输入:
1.txt
【 wlan.fc 】
【 wlan.fc.version 】
【 wlan.fc.type 】
【 wlan.fc.subtype 】
【 wlan.fc.type_subtype 】
【 wlan.fc.extension 】
2.txt
{"Frame Control Field" 【 wlan.fc 】
{"Version" 【 wlan.fc.version 】
{"Type" 【 wlan.fc.type 】
{"Subtype" 【 wlan.fc.subtype 】
{"Type/Subtype" 【 wlan.fc.type_subtype 】
{"Control Frame Extension" 【 wlan.fc.extension 】
输出:
out.txt
【 wlan.fc 】 {"Frame Control Field" 【 wlan.fc 】
【 wlan.fc.version 】 {"Version" 【 wlan.fc.version 】
【 wlan.fc.type 】 {"Type" 【 wlan.fc.type 】
【 wlan.fc.subtype 】 {"Subtype" 【 wlan.fc.subtype 】
【 wlan.fc.type_subtype 】 {"Type/Subtype" 【 wlan.fc.type_subtype 】
J
K
L
LinkList对应的linknode的逆序 Java实现
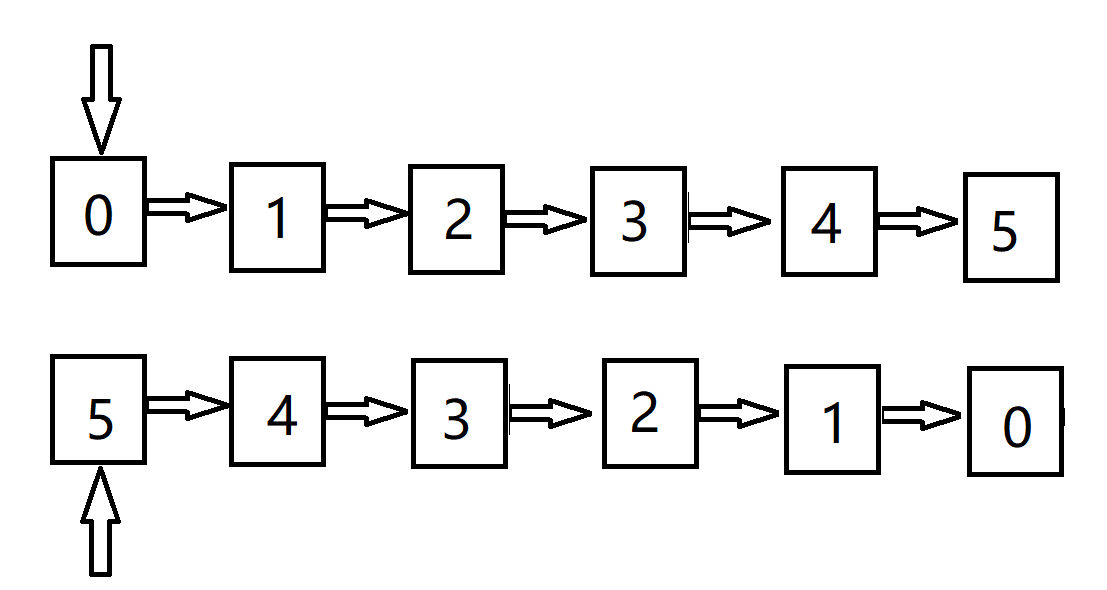
思路: 把linkList分为新旧两个链表 分别更新新旧链表的表头
同时需要把当前操作的node 添加的新链表的头结点之前 使其成为新的表头
重点代码:
LinkNode newHead = head;
LinkNode newHeadTail = head;
LinkNode oldHead = head;
while(oldHead != null )
{
LinkNode cur = oldHead; // 获得当前操作的 LinkNode
oldHead = cur.next; // 设置oldHead 新的起点
// 相当于的头指针前加一个node 使得这个node 变成头指针
LinkNode newHeadTemp = newHeadTail; // 保存当前的头结点
newHeadTail = cur ; // 对当前的Node进行处理 新的尾巴
newHeadTail.next = newHeadTemp; // CurNode 和 newHeadTail 建立关系
}
newHead.next = null;
public class LinkNode {
public int value;
public LinkNode next;
}
public class ReverseListObj {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkNode head = new LinkNode();
head.value = 0;
head.next = null;
LinkNode temp = head;
for(int i=1;i<10;i++) {
LinkNode node = new LinkNode();
node.value = i;
node.next = null;
temp.next = node;
temp = node;
}
System.out.println("============main printList 打印原始Link结点 Begin=================");
printList(head);
System.out.println("============main printList 打印原始Link结点 End=================");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("========main printReverseList_Stack 使用堆栈逆序打印LinkList Begin======");
printReverseList_Stack(head);
System.out.println("========main printReverseList_Stack 使用堆栈逆序打印LinkList End======");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("========main printReverseList_Recursion 使用递归逆序打印LinkList Begin======");
printReverseList_Recursion(head);
System.out.println("========main printReverseList_Recursion 使用递归逆序打印LinkList End======");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("========main reverseLinkNodeList 对当前的LinkList进行逆序重排 头尾交换 Begin======");
LinkNode newHead = reverseLinkNodeList(head);
printList(newHead);
System.out.println("========main reverseLinkNodeList 对当前的LinkList进行逆序重排 头尾交换 End======");
}
/**
*
* @Title: reverseLinkNodeList
* @Description: 对链表进行逆序使得由头变为 由尾变头
* @param LinkNode head
* @return LinkNode newHead
* @throws
*/
public static LinkNode reverseLinkNodeList(LinkNode head)
{
System.out.println("===============reverseLinkNodeList Begin=================");
if(head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
LinkNode newHead = head;
LinkNode newHeadTail = head;
LinkNode oldHead = head;
while(oldHead != null )
{
LinkNode cur = oldHead; // 获得当前操作的 LinkNode
oldHead = cur.next; // 设置oldHead 新的起点
// 相当于的头指针前加一个node 使得这个node 变成头指针
LinkNode newHeadTemp = newHeadTail; // 保存当前的头结点
newHeadTail = cur ; // 对当前的Node进行处理 新的尾巴
newHeadTail.next = newHeadTemp; // CurNode 和 newHeadTail 建立关系
}
newHead.next = null;
System.out.println("===============reverseLinkNodeList End=================");
return newHeadTail;
}
/**
*
* @Title: printList
* @Description: 正常输出链表(递归实现)
* @param head
* @return void
* @throws
*/
private static void printList(LinkNode head) {
System.out.println("===============printList Begin=================");
if(head==null)return;
LinkNode mLinkNode= head;
while(mLinkNode.next!=null) {
System.out.print(mLinkNode.value+" ");
mLinkNode = mLinkNode.next;
}
System.out.print(mLinkNode.value+" ");
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("===============printList End=================");
}
/**
*
* @Title: printReverseList_Recursion
* @Description: 反向输出链表(递归实现)
* @param head
* @return void
* @throws
*/
private static void printReverseList_Recursion(LinkNode head) {
if(head==null)return;
if(head.next!=null) {
printReverseList_Recursion(head.next);
}
System.out.print(head.value+" ");
}
/**
*
* @Title: printReverseList
* @Description:反向输出链表 (栈实现)
* @param head
* @return void
* @throws
*/
private static void printReverseList_Stack(LinkNode head) {
System.out.println("===============printReverseList_Stack Begin=================");
if(head == null) return;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack();
// 遍历链表
LinkNode temp = head;
while(temp != null) {
stack.add(temp.value);
temp = temp.next;
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
if(stack.size()!=1) {
System.out.print(stack.pop()+",");
}else {
System.out.print(stack.pop());
}
}
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("===============printReverseList_Stack End=================");
}
}
/*
输出:
============main printList 打印原始Link结点 Begin=================
===============printList Begin=================
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
===============printList End=================
============main printList 打印原始Link结点 End=================
========main printReverseList_Stack 使用堆栈逆序打印LinkList Begin======
===============printReverseList_Stack Begin=================
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0
===============printReverseList_Stack End=================
========main printReverseList_Stack 使用堆栈逆序打印LinkList End======
========main printReverseList_Recursion 使用递归逆序打印LinkList Begin======
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ========main printReverseList_Recursion 使用递归逆序打印LinkList End======
========main reverseLinkNodeList 对当前的LinkList进行逆序重排 头尾交换 Begin======
===============reverseLinkNodeList Begin=================
===============reverseLinkNodeList End=================
===============printList Begin=================
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
===============printList End=================
========main reverseLinkNodeList 对当前的LinkList进行逆序重排 头尾交换 End======
*/
M
N
内存泄漏
内存泄漏有两种情况:
1: 一种情况如在C/C++语言中的,在堆中的分配的内存,在没有将其释放掉的时候,就将所有能访问这块内存的方式都删掉(如指针重新赋值)
2: 另一种情况则是在内存对象明明已经不需要的时候,还仍然保留着这块内存和它的访问方式(引用)
第一种情况,在Java中已经由于垃圾回收机制的引入,得到了很好的解决。所以,Java中的内存泄漏,主要指的是第二种情况
内存泄漏的例子:
Vector v=new Vector(10);
for (int i=1;i<100; i++){
Object o=new Object();
v.add(o);
o=null;
}
Vector的容量之所以重要,有以下两个原因:
1. 容器的大小一旦超过capacity的大小,vector会重新配置内部的存储器,导致和vector元素相关的所有reference、pointers、iterator都会失效。
分析:
代码栈中存在引用 Vector v 和 引用 Object o
在For循环中,我们不断的生成新的对象,然后将其添加到Vector对象中,之后将o引用置空
问题是当o引用被置空后,如果发生GC,我们创建的Object对象是否能够被GC回收呢?
答案是否定的。 GC不能收回Object对象。
因为,GC在跟踪代码栈中的引用时,会发现v引用,而继续往下跟踪,就会发现v引用指向的内存空间中又存在指向Object对象的引用。
也就是说尽管o引用已经被置空,但是Object对象仍然存在其他的引用,是可以被访问到的,所以GC无法将其释放掉。
因此,如果对象加入到Vector 后,还必须从 Vector 中删除,最简单的方法就是将 Vector 对象设置为 null。
内存泄漏分类:
1、静态集合类引起内存泄漏:
像HashMap、Vector等的使用最容易出现内存泄露,这些静态变量的生命周期和应用程序一致,他们所引用的所有的对象Object也不能被释放,因为他们也将一直被Vector等引用着。
2.各种连接
3. Handler 造成的内存泄漏
Handler 发送的 Message 尚未被处理,则该 Message 及发送它的 Handler 对象将被线程 MessageQueue 一直持有。
由于 Handler 属于 TLS(Thread Local Storage) 变量, 生命周期和 Activity 是不一致的。因此这种实现方式一般很难保证跟 View 或者 Activity 的生命周期保持一致,故很容易导致无法正确释放。
O
override(覆盖) overload(重载) overwrite(重写)
区别:
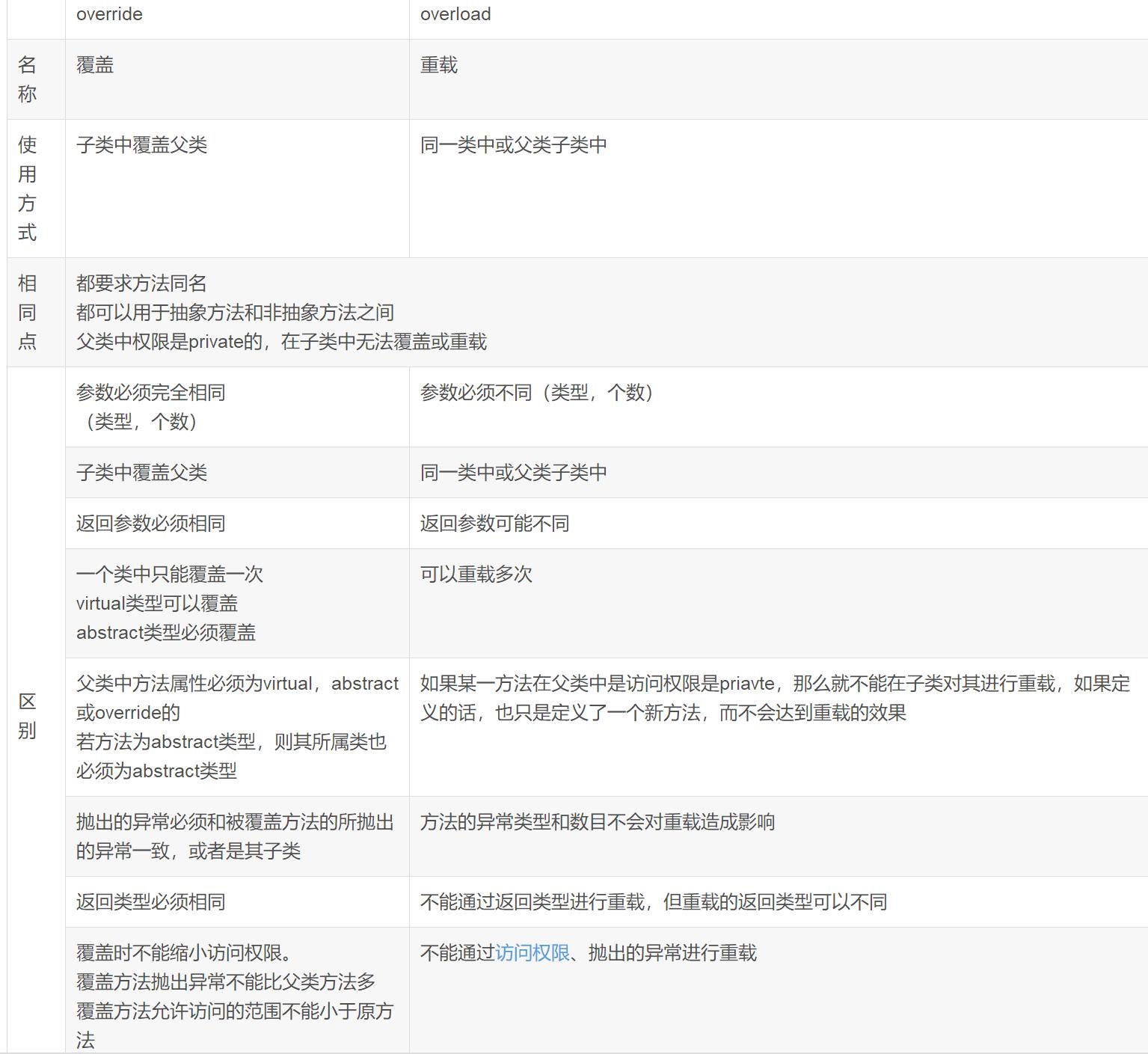 覆盖 override 的情况汇总:
覆盖 override 的情况汇总:
覆盖(override):
继承了父类的同名无參函数:当子类从父类继承一个无參方法,而又定义了一个同样的无参数的方法时,
则子类新写的方法覆盖父类的方法,成为覆盖。 【 override 覆盖】
Class Father{ Methid(); static Static_Method()};
Class Child extend Father{Methid();}; // 非静态内部类无法编写 静态方法
Class static StaticChild extend Father{ Methid(); static Static_Method() };
总结:
1. 父类引用非静态子类 Father fatherRef = new Child();
fatherRef.Method() 输出===》 Child_Method
fatherRef.Static_Method() 输出===》 Father_Static_Method
2. 子类引用非静态子类 Child childRef = new Child();
childRef.Method() 输出===》 Child_Method
childRef.Static_Method() 输出===》 Father_Static_Method
3. 父类引用静态子类 Father fatherRef_static = new StaticChild();
fatherRef_static.Method() 输出===》 StaticChild_Method
fatherRef_static.Static_Method() 输出===》 Father_Static_Method
4. 子类引用静态子类 StaticChild childRef_static = new StaticChild();
childRef_static.Method() 输出===》 StaticChild_Method
childRef_static.Static_Method() 输出===》 StaticChild_Static_Method
例子:
package test;
public class OverrideObjFather {
public void zukgitMethod(){
System.out.println("OverrideObjFather.zukgitMethod_Object");
}
public static void zukgitMethod_static(){
System.out.println("OverrideObjFather.zukgitMethod_StaticClass");
}
public class OverrideObjChildObj extends OverrideObjFather{
public void zukgitMethod(){
System.out.println("OverrideObjChildObj.zukgitMethod_Object");
}
}
public static class OverrideObjChildStaticClass extends OverrideObjFather{
public void zukgitMethod(){
System.out.println("OverrideObjChildStaticClass.zukgitMethod_Object");
}
public static void zukgitMethod_static(){
System.out.println("OverrideObjChildStaticClass.zukgitMethod_StaticClass");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("==================Father f = new Child(); 父类引用指向子类 Begin===========");
OverrideObjFather fatherRefChild = (new OverrideObjFather()).new OverrideObjChildObj();
System.out.println("==========父类引用子类对象.zukgitMethod() begin ========");
fatherRefChild.zukgitMethod();
System.out.println("==========父类引用子类对象.zukgitMethod() end ========");
System.out.println("==========父类引用子类对象.zukgitMethod_static() begin ========");
fatherRefChild.zukgitMethod_static();
System.out.println("==========父类引用子类对象.zukgitMethod_static() end ========");
System.out.println("==================Father f = new Child(); 父类引用指向子类 End===========");
System.out.println("==================Child c = new Child(); 子类引用指向子类 Begin========");
OverrideObjChildObj childRefChild = (new OverrideObjFather()).new OverrideObjChildObj();
System.out.println("==========子类引用子类静态对象.zukgitMethod() begin ========");
childRefChild.zukgitMethod();
System.out.println("==========子类引用子类静态对象.zukgitMethod() end ========");
System.out.println("==========子类引用子类静态对象.zukgitMethod_static() begin ========");
childRefChild.zukgitMethod_static();
System.out.println("==========子类引用子类静态对象.zukgitMethod_static() end ========");
System.out.println("==================Child c = new Child(); 子类引用指向子类 End========");
System.out.println("#################################################");
System.out.println("==================Father f = new Child_Static(); 父类引用指向静态子类对象 Begin===========");
OverrideObjFather fatherRefChild_Static = new OverrideObjFather.OverrideObjChildStaticClass();
System.out.println("==========父类引用静态子类对象.zukgitMethod() begin ========");
fatherRefChild_Static.zukgitMethod();
System.out.println("==========父类引用静态子类对象.zukgitMethod() end ========");
System.out.println("==========父类引用静态子类对象.zukgitMethod_static() begin ========");
fatherRefChild_Static.zukgitMethod_static();
System.out.println("==========父类引用静态子类对象.zukgitMethod_static() end ========");
System.out.println("==================Father f = new Child_Static(); 父类引用指向静态子类对象 End===========");
System.out.println("==================Child c = new Child()_Static; 子类引用指向子类 Begin========");
OverrideObjChildStaticClass childRefChild_Static = new OverrideObjFather.OverrideObjChildStaticClass();
System.out.println("==================Child c = new Child()_Static; zukgitMethod Begin========");
childRefChild_Static.zukgitMethod();
System.out.println("==================Child c = new Child()_Static; zukgitMethod End========");
System.out.println("==================Child c = new Child()_Static; zukgitMethod_static Begin========");
childRefChild_Static.zukgitMethod_static();
System.out.println("==================Child c = new Child()_Static; zukgitMethod_static End========");
System.out.println("==================Child c = new Child()_Static; 子类引用指向子类 Begin========");
}
}
/*
输出
==================Father f = new Child(); 父类引用指向子类 Begin===========
==========父类引用子类对象.zukgitMethod() begin ========
OverrideObjChildObj.zukgitMethod_Object
==========父类引用子类对象.zukgitMethod() end ========
==========父类引用子类对象.zukgitMethod_static() begin ========
OverrideObjFather.zukgitMethod_StaticClass
==========父类引用子类对象.zukgitMethod_static() end ========
==================Father f = new Child(); 父类引用指向子类 End===========
==================Child c = new Child(); 子类引用指向子类 Begin========
==========子类引用子类静态对象.zukgitMethod() begin ========
OverrideObjChildObj.zukgitMethod_Object
==========子类引用子类静态对象.zukgitMethod() end ========
==========子类引用子类静态对象.zukgitMethod_static() begin ========
OverrideObjFather.zukgitMethod_StaticClass
==========子类引用子类静态对象.zukgitMethod_static() end ========
==================Child c = new Child(); 子类引用指向子类 End========
#################################################
==================Father f = new Child_Static(); 父类引用指向静态子类对象 Begin===========
==========父类引用静态子类对象.zukgitMethod() begin ========
OverrideObjChildStaticClass.zukgitMethod_Object
==========父类引用静态子类对象.zukgitMethod() end ========
==========父类引用静态子类对象.zukgitMethod_static() begin ========
OverrideObjFather.zukgitMethod_StaticClass
==========父类引用静态子类对象.zukgitMethod_static() end ========
==================Father f = new Child_Static(); 父类引用指向静态子类对象 End===========
==================Child c = new Child()_Static; 子类引用指向子类 Begin========
==================Child c = new Child()_Static; zukgitMethod Begin========
OverrideObjChildStaticClass.zukgitMethod_Object
==================Child c = new Child()_Static; zukgitMethod End========
==================Child c = new Child()_Static; zukgitMethod_static Begin========
OverrideObjChildStaticClass.zukgitMethod_StaticClass
==================Child c = new Child()_Static; zukgitMethod_static End========
==================Child c = new Child()_Static; 子类引用指向子类 Begin========
*/
重载Overload: 同名不同参数
package test;
public class OverLoadObj { // overload 重载
public void doSomeThing(int a) {
System.out.println("OverLoadObj doSomeThing a=:" + a);
}
public void doSomeThing(int a , int b) { // 同一个类之间的重载
System.out.println("OverLoadObj doSomeThing a=:" + a+ ", b = " + b);
}
class OverLoadObj_SubClass extends OverLoadObj {
public void doSomeThing(int a, int b , int c) { // 父子类之间的重载
System.out.println("OverLoadObj_SubClass doSomeThing: a" + a + ", b = " + b+ " , c ="+c);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
OverLoadObj_SubClass sub = (new OverLoadObj()).new OverLoadObj_SubClass();
sub.doSomeThing(0);
sub.doSomeThing(1, 2 , 3);
}
}
/* 输出:
OverLoadObj doSomeThing a=:0
OverLoadObj_SubClass doSomeThing: a1, b = 2 , c =3
*/
Orientation 方向与Activity生命周期
AndroidManifest.xml 文件中 可定义 android:screenOrientation 和 android:configChanges属性如下:
<activity android:screenOrientation="sensor"> </activity>
<activity android:configChanges="screenSize|keyboardHidden"> </activity>
android:screenOrientation 属性说明:
在开发android的应用中,有时候需要限制横竖屏切换。只需要在AndroidManifest.xml文件中加入android:screenOrientation属性限制,例如游戏只能横屏。
android:configChanges属性说明:
android中的组件Activity在manifest.xml文件中可以指定参数android:ConfigChanges,用于捕获手机状态的改变
在Activity中添加了android:configChanges属性,在当所指定属性(Configuration Changes)发生改变时,通知程序调用 onConfigurationChanged()函数。
对android:configChanges属性,一般认为有以下几点:
1、不设置Activity的android:configChanges时,切屏会重新调用各个生命周期,切横屏时会执行一次,切竖屏时会执行两次
2、设置Activity的android:configChanges="orientation"时,切屏还是会重新调用各个生命周期,切横、竖屏时只会执行一次
3、设置Activity的android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden|screenSize"时,切屏不会重新调用各个生命周期,只会执行onConfigurationChanged方法
Android 3.2 API13之后 screen size也开始跟着设备的横竖切换而改变 ,所以如果要切换时不销毁Activity 需要额外加入 android:configChanges="screenSize"


android:screenOrientation 可选值集合如下:
...\Android\sdk\platforms\android-25\data\res\values\attrs_manifest.xml 文件中定义了 android:screenOrientation 属性的可选值
<attr name="screenOrientation">
<enum name="unspecified" value="-1" />
<enum name="landscape" value="0" />
<enum name="portrait" value="1" />
<enum name="user" value="2" />
<enum name="behind" value="3" />
<enum name="sensor" value="4" />
<enum name="nosensor" value="5" />
<enum name="sensorLandscape" value="6" />
<enum name="sensorPortrait" value="7" />
<enum name="reverseLandscape" value="8" />
<enum name="reversePortrait" value="9" />
<enum name="fullSensor" value="10" />
<enum name="userLandscape" value="11" />
<enum name="userPortrait" value="12" />
<enum name="fullUser" value="13" />
<enum name="locked" value="14" />
</attr>
android:configChanges 可选值集合如下:
...\Android\sdk\platforms\android-25\data\res\values\attrs_manifest.xml 文件中定义了 android:configChanges 属性的可选值
<attr name="configChanges">
<flag name="mcc" value="0x0001" />
<flag name="mnc" value="0x0002" />
<flag name="locale" value="0x0004" />
<flag name="touchscreen" value="0x0008" />
<flag name="keyboard" value="0x0010" />
<flag name="keyboardHidden" value="0x0020" />
<flag name="navigation" value="0x0040" />
<flag name="orientation" value="0x0080" />
<flag name="screenLayout" value="0x0100" />
<flag name="uiMode" value="0x0200" />
<flag name="screenSize" value="0x0400" />
<flag name="smallestScreenSize" value="0x0800" />
<flag name="density" value="0x1000" />
<flag name="layoutDirection" value="0x2000" />
<flag name="fontScale" value="0x40000000" />
</attr>
设置-自动旋转:
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/provider/Settings.java
手机设置Settings数据库中 含有 Settings.System.ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION 是否开启重力感应开关
Settings.System.ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION 来决定 是否依据重力感应旋转屏幕,使得屏幕显示总是正对着用户
public static final String ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION = "accelerometer_rotation";
Settings.System.putInt(context.getContentResolver(),Settings.System.ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION,1) 开启 自动旋转
Settings.System.putInt(context.getContentResolver(),Settings.System.ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION,0) 关闭 自动旋转
P
public
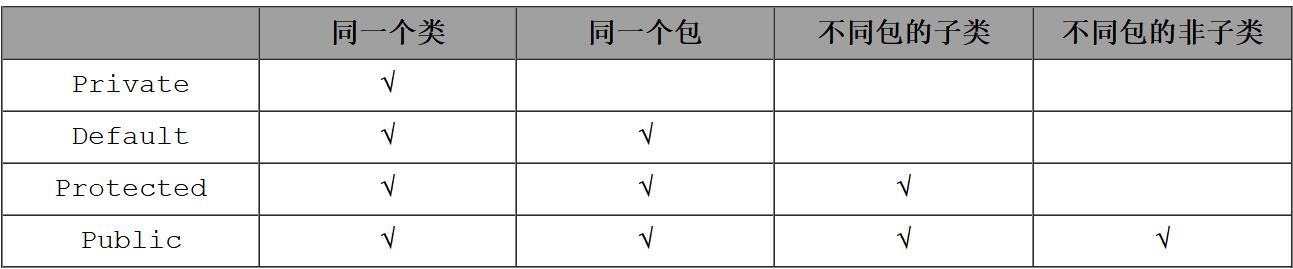
Q
R
S
SharePreference 的异步apply写入磁盘操作 同步commit写入磁盘操作
SharedPreferences(后续简称SP)为我们提供了轻量级存储能力,方便了少量数据的持久化。
SharedPreferences保存数据,其背后是用xml文件存放数据,文件存放在/data/data/<package name>/shared_prefs目录下:
但是由于项目越来越庞大,SP操作使用不当会导致app卡顿,乃至ANR问题。
SP性能优化点
SP性能变差的原因有很多。
1.原生API的限制主要有以下两方面:
(1)IO瓶颈
(2)锁性能差
2.对SP的不当封装也会间接造成数据读写性能差。
SharedPreferences数据写入磁盘也有两个方法会触发:
(1)Editor的commit方法,每次执行时同步写入磁盘。
(2)Editor的apply方法,每次执行时在单线程池中加入写入磁盘Task,异步写入。
commit和apply的方法区别在于同步写入和异步写入,以及是否需要返回值。
在不需要返回值的情况下,使用apply方法可以极大的提高性能。
同时,多个写入操作可以合并为一个commit/apply,将多个写入操作合并后也能提高IO性能。
public interface SharedPreferences {
void registerOnSharedPreferenceChangeListener(SharedPreferences.OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener var1); 【 注册 SharePreference 变化监听器 】
void unregisterOnSharedPreferenceChangeListener(SharedPreferences.OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener var1);
public interface OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener {
void onSharedPreferenceChanged(SharedPreferences var1, String var2);
}
String getString(String var1, String var2); 【 SharedPreferences 用于读取数据的方法】
Set<String> getStringSet(String var1, Set<String> var2);
int getInt(String var1, int var2);
long getLong(String var1, long var2);
float getFloat(String var1, float var2);
boolean getBoolean(String var1, boolean var2);
boolean contains(String var1);
public interface Editor { // 【SharedPreferences.Editor 是专门用来写数据的类】
SharedPreferences.Editor putString(String var1, String var2);
SharedPreferences.Editor putStringSet(String var1, Set<String> var2);
SharedPreferences.Editor putInt(String var1, int var2);
SharedPreferences.Editor putLong(String var1, long var2);
SharedPreferences.Editor putFloat(String var1, float var2);
SharedPreferences.Editor putBoolean(String var1, boolean var2);
SharedPreferences.Editor remove(String var1);
SharedPreferences.Editor clear();
boolean commit(); // 同步写入磁盘操作 程序需要等待运行结果返回 判断是否写入成功
void apply(); // 异步写入磁盘操作 没有返回值
}
}
使用SharePreference的方法:
【1. 创建SharePreference 并写入数据】
// Context.getSharedPreferences
SharedPreferences mSharedPreferences = getSharedPreferences("zukgit", Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
Editor editor = mSharedPreferences.edit();
editor.putInt("user_id", 1);
editor.putString("user_mobile","13811111111");
editor.commit();
【2. 读取SharePreference 的方法 】
SharedPreferences share=getSharedPreferences("zukgit",Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE);
String str=share.getString("str","");
HashSet<String> set = share.getStringSet("stringArr", null);
int i=share.getInt("i",0);
long longValue = share.getLong("longValue", 0L);
float floatValue = getFloat("floatValue", 0.0f);
boolean flag=share.getBoolean("flag",false);
SharedPreferences实例:
@Override
protected void onStart() {
// 在 /data/data/<package_name>/shared_prefs 创建一个名字为 zukgit 的 xml文件 模式 MODE_PRIVATE 目前新版本只有该一种模式
SharedPreferences mSP = getSharedPreferences("zukgit",MODE_PRIVATE);
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = mSP.edit();
editor.putBoolean("zukgit_isMan", true);
editor.putInt("zukgit_ID", 1);
editor.putString("zukgit_Name", "zukgit");
Set set= new HashSet<String>();
set.add("zzq");
set.add("zwt");
editor.putStringSet("zukgit_brothers", set );
editor.putLong("zukgit_livingDay", 26*365 );
editor.putFloat("zukgit_PI", 3.14f);
boolean flag = editor.commit(); // 同步提交 有返回值 boolean 表示提交是否成功
// editor.apply(); 异步提交到磁盘 无返回值
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
boolean booleanValue = mSP.getBoolean("zukgit_isMan",false);
int intValue = mSP.getInt("zukgit_ID",0);
String stringValue = mSP.getString("zukgit_Name","");
HashSet<String> hashSetValue = (HashSet<String>) mSP.getStringSet("zukgit_brothers",null);
long longValue = mSP.getLong("zukgit_livingDay",0L);
float floatValue = mSP.getFloat("zukgit_PI",0F);
android.util.Log.i("zukgit",booleanValue?" booleanValue==true":" booleanValue==false");
android.util.Log.i("zukgit","intValue == "+ intValue);
android.util.Log.i("zukgit","stringValue == "+ stringValue);
android.util.Log.i("zukgit","hashSetValue == "+ Arrays.toString(hashSetValue.toArray()));
android.util.Log.i("zukgit","longValue == "+ longValue);
android.util.Log.i("zukgit","floatValue == "+ floatValue);
}
打印Log:
I/zukgit: booleanValue==true
I/zukgit: intValue == 1
I/zukgit: stringValue == zukgit
I/zukgit: hashSetValue == [zwt, zzq]
I/zukgit: longValue == 9490
I/zukgit: floatValue == 3.14
生成的文件为:
/data/data/xxxxxxxx/shared_prefs/zukgit.xml
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8' standalone='yes' ?>
<map>
<set name="zukgit_brothers">
<string>zwt</string>
<string>zzq</string>
</set>
<int name="zukgit_ID" value="1" />
<string name="zukgit_Name">zukgit</string>
<long name="zukgit_livingDay" value="9490" />
<float name="zukgit_PI" value="3.14" />
<boolean name="zukgit_isMan" value="true" />
</map>
String产生对象问题
对于字符串: 其对象的引用都是存储在栈中的 String s Static String s 都是, 如果是【编译期已经创建好(直接用双引号定义的)的就存储在常量池中】 包括 Static String s=”Hello World” method(){ String str=”Hello World”} new String(“Hello World”) 中的”” 引号内字符串 如果是【运行期(new出来的)才能确定的就存储在堆中】。对于equals相等的字符串,在常量池中永远只有一份,在堆中有多份。 new String() 存储在堆中
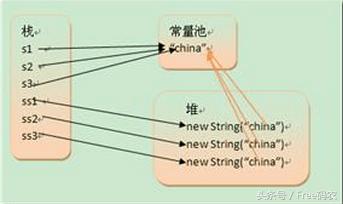
public class String_Test {
static String static_str1 = "Hello World!"; // 静态字符串 存储在常量池 并且 只会有一个对象
static String static_str2 = "Hello World!"; // static_str1 和 static_str2 都指向 常量池常量 "Hello World!"
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 以常量池中的 "Hello World!" 创建一个 堆中的 String对象 ,如果常量池没有"" 引号对象 那么就会在常量池创建 如 "Hello Zukgit!"
String str1 = new String("Hello World!");
String str2 = new String("Hello World!");
String str3 ="Hello World!";
String str4 ="Hello Zukgit!"; // 将会在常量池中创建 对象
System.out.println(static_str1 =="Hello World!" ? "static_str1 ==\"Hello World!\"":"static_str1 !=\"Hello World!\"");
System.out.println(static_str1 ==static_str2 ? "static_str1 ==static_str1":"static_str1 !=static_str2");
System.out.println(static_str2 =="Hello World!" ? "static_str2 ==\"Hello World!\"":"static_str2 !=\"Hello World!\"");
System.out.println(static_str1 ==str1 ? "static_str1 ==str1":"static_str1 !=str1");
System.out.println(str1 ==str2 ? "str1 ==str2":"str1 !=str2"); System.out.println(str1 ==str3 ? "str1 ==str3":"str1 !=str3");
System.out.println(str2 ==str3 ? "str2 ==str3":"str2 !=str3");
System.out.println(static_str1 ==str3 ? "static_str1 ==str3":"static_str1 !=str3");
System.out.println(static_str2 ==str3 ? "static_str2 ==str3":"static_str2 !=str3");
}
}
/*
* 输出:
*
static_str1 =="Hello World!" //【常量池中的 对象 相等】
static_str1 ==static_str1 //【常量池中的 对象 相等】
static_str2 =="Hello World!" //【常量池中的 对象 相等】
static_str1 !=str1 // 【常量池中的对象static_str1 与 堆中的对象str1 不相等 】
str1 !=str2 // 【堆中的对象str1 与 堆中的对象str2 是两个对象 内存地址不相等 】
str1 !=str3 // 【堆中的对象str1 与 堆中的对象str2 是两个对象 内存地址不相等 】
str2 !=str3 // 【堆中的对象str1 与 堆中的对象str2 是两个对象 内存地址不相等 】
static_str1 ==str3 //【常量池中的 对象 相等】
static_str2 ==str3 //【常量池中的 对象 相等】
*
*
*
* */
Syncronized 关键字
synchronized关键字涉及到锁的概念,Syncronized 主要解决多线程安全问题、
synchronized(this) ,如果一个线程进入到一个 synchronized(this) 修饰的方法块中,那么所有其他线程遇到的所有包含的synchronized(this) 方法 都被阻塞,直到获得锁才能继续执行。
对象锁synchronized作用域: 对象锁默认 synchronized(this)
【 对象锁的synchronized 】修饰方法和代码块 即对象方法,即非静态的new出来的对象的方法
1.修饰方法 public synchronized void syncMethod(){ ... }
2.修饰方法块 public synchronized void Method(){ synchronized(this){ xxxx }}
类锁synchronized作用域: 类锁synchronized 默认是 synchronized(TestSynchronized.class)
1.类锁修饰对象方法
public void ObjectMethod()
{
synchronized(TestSynchronized.class) // 类锁
{
xxxxxx
}
}
2.对象锁修饰静态方法 默认是 synchronize(TestSynchronized.class)
public static synchronized void static_Method() {
}
对象锁案例:
package test;
public class ThreadTest {
int i = 0 ;
//【20个线程 同一时间段只能有一个线程执行 对象锁synchronized修饰的方法( 或者 add() 或者 delete())】
// 对象锁synchronized 修饰的方法在一个线程执行拿到锁后 其余的所有其他对象锁synchronized 修饰的方法都会上锁
// 并不自己之前认为的方法执行到 synchronized void add() 所有线程等待在该方法外 其余 synchronized 方法不受影响
// 即 ThradA.add() 执行后 阻塞了ThradB.add() 方法, 并且也会阻塞到 ThreadC.delete() 方法,
public synchronized void add(){
Thread curThread = Thread.currentThread();
String ThradName = curThread.getName();
for (int k = 0; k <10; k++) {
System.out.println(ThradName+" --add-- "+i++);
}
}
public synchronized void delete(){
Thread curThread = Thread.currentThread();
String ThradName = curThread.getName();
for (int k = 0; k <10; k++) {
System.out.println(ThradName+" --delete-- "+i--);
}
}
/* public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread addThread;
Thread deleteThread;
ThreadTest mThreadTest = new ThreadTest();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
addThread = new Thread(mThreadTest.new RunnableAdd());
addThread.start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
deleteThread = new Thread(mThreadTest.new RunnableDelete());
deleteThread.start();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread addThread;
Thread deleteThread;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//【由于线程每次new 都是new的 新的对象ThreadTest 导致 每个线程各自有各自的锁,这个锁不是同一个】
//【这样将导致 synchronized关键字无用 并且每个 新的对象ThreadTest 都有自己的值 】
addThread = new Thread(new ThreadTest().new RunnableAdd());
addThread.start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
deleteThread = new Thread(new ThreadTest().new RunnableDelete());
deleteThread.start();
}
}
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread addThread;
Thread deleteThread;
ThreadTest mThreadTest = new ThreadTest();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//【使用mThreadTest 来创建 Runnable匿名类 使得所有线程的锁 都是一致的 A线程拿到锁执行 那么必然其他的线程只能阻塞】
addThread = new Thread(mThreadTest.new RunnableAdd());
addThread.start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
deleteThread = new Thread(mThreadTest.new RunnableDelete());
deleteThread.start();
}
}
public class RunnableAdd implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
add();
}
}
public class RunnableDelete implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
delete();
}
}
}
类锁案例:
public class ThreadTest {
// int value = 0 ;
// 由于在该案例中 main函数中的 Thread 是通过 new 出 不同的 ThreadTest() 对象实例 每一个对象 都有一个 int value = 0 ;
// 所以各个线程通过 synchronized(ThreadTest.class) 类锁依次执行 但是 每个线程都有独立的 value 所以导致 value 要么是 99 add()函数 要么是-99 delete函数
static int value = 0 ; // 为了让多有对象共享一个副本 把变量 value 改为 静态的 之后就能符合预期
//【20个线程 同一时间段只能有一个线程执行 对象锁synchronized修饰的方法( 或者 add() 或者 delete())】
// 对象锁synchronized 修饰的方法在一个线程执行拿到锁后 其余的所有其他对象锁synchronized 修饰的方法都会上锁
// 并不自己之前认为的方法执行到 synchronized void add() 所有线程等待在该方法外 其余 synchronized 方法不受影响
// 即 ThradA.add() 执行后 阻塞了ThradB.add() 方法, bingq也会阻塞到 ThreadC.delete() 方法,
public synchronized void add(){
Thread curThread = Thread.currentThread();
String ThradName = curThread.getName();
synchronized(ThreadTest.class){
for (int k = 0; k <100; k++) {
System.out.println(ThradName+" --add-- "+value++);
}
}
}
public void delete(){
Thread curThread = Thread.currentThread();
String ThradName = curThread.getName();
synchronized(ThreadTest.class){
for (int k = 0; k <100; k++) {
System.out.println(ThradName+" --delete-- "+value--);
}
}
}
/*
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread addThread;
Thread deleteThread;
ThreadTest mThreadTest = new ThreadTest();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//【使用mThreadTest 来创建 Runnable匿名类 使得所有线程的锁 都是一致的 A线程拿到锁执行 那么必然其他的线程只能阻塞】
addThread = new Thread(mThreadTest.new RunnableAdd());
addThread.start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
deleteThread = new Thread(mThreadTest.new RunnableDelete());
deleteThread.start();
}
}
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread addThread;
Thread deleteThread;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//【由于线程每次new 都是new的 新的对象ThreadTest 导致 每个线程各自有各自的锁,这个锁不是同一个】
//【这样将导致 synchronized关键字无用 并且每个 新的对象ThreadTest 都有自己的值 】
addThread = new Thread(new ThreadTest().new RunnableAdd());
addThread.start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
deleteThread = new Thread(new ThreadTest().new RunnableDelete());
deleteThread.start();
}
}
public class RunnableAdd implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
add();
}
}
public class RunnableDelete implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
delete();
}
}
}
int value = 0 时:Value是非静态时输出 (value 每个对象都有 所以value并不共享 是单独的 所以 add后是 4 delete后是 -4)
输出:
Thread-4 --add-- 0
Thread-4 --add-- 1
Thread-4 --add-- 2
Thread-4 --add-- 3
Thread-4 --add-- 4
Thread-13 --delete-- 0
Thread-13 --delete-- -1
Thread-13 --delete-- -2
Thread-13 --delete-- -3
Thread-13 --delete-- -4
Thread-3 --add-- 0
Thread-3 --add-- 1
Thread-3 --add-- 2
Thread-3 --add-- 3
Thread-3 --add-- 4
static int value = 0 时:Value是静态时输出
输出:
Thread-0 --add-- 40
Thread-0 --add-- 41
Thread-0 --add-- 42
Thread-0 --add-- 43
Thread-0 --add-- 44
Thread-10 --delete-- 45
Thread-10 --delete-- 44
Thread-10 --delete-- 43
Thread-10 --delete-- 42
Thread-10 --delete-- 41
Thread-9 --add-- 40
Thread-9 --add-- 41
Thread-9 --add-- 42
Thread-9 --add-- 43
Thread-9 --add-- 44
Synchronized 与 wait() 多生产者消费者场景
/*当操作线程的状态,如wait(),notify()等,如果没有给其加上同步方法,此时就会引起该异常。
* 加上synchronizied关键字,将其编程同步代码块或同步方法,该异常消失。
*
*
* synchronized (this) { wait()} 当线程执行到同步代码块中的 wait()时 本线程会阻塞,并且交出 synchronized 锁
* 当其他地方调用到 notify() 时会唤醒当前线程,但是如果还是得不到锁 那么当前线程仍然继续阻塞
*
*/
public class SyncAndWaitTest {
public static Object addObjectLock = new Object();
public static Object deleteObjectLock = new Object();
public volatile int value = 0;
public static int VectorSize = 10;
public static int AdderNumer = 3;
public static int DeleteNumer = 3;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("==============main begin===============");
SyncAndWaitTest obj = new SyncAndWaitTest();
for (int i = 0; i < AdderNumer; i++) {
new Thread(obj.new RunnableAdd()).start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < DeleteNumer; i++) {
new Thread(obj.new RunnableDelete()).start();
}
System.out.println("==============main end===============");
}
public void add() {
Thread curThread = Thread.currentThread();
String ThradName = curThread.getName();
while (true) {
synchronized (this) {
while (value >= VectorSize) {
try {
notifyAll();
System.out.println("~~~~~~ThradName(add)=" + ThradName +" wait() begin~~~~~~~");
wait();
System.out.println("~~~~~~ThradName(add)=" + ThradName +" wait() end~~~~~~~");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
synchronized (this) {
if (value >= 1) {
System.out.println("##### ThradName(add) " + ThradName +" value >= 1 notifyAll() 通知消费者消费 begin #####");
notifyAll();
System.out.println("##### ThradName(add) " + ThradName +" value >= 1 notifyAll() 通知消费者消费 end #####");
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
int oldValue = 0;
int newValue = 0;
synchronized (addObjectLock) {
if (value < VectorSize) {
oldValue = value;
value++;
newValue = value;
}
}
if (oldValue == 0 && newValue == 0) {
System.out.println("ThradName(add)=" + ThradName + " 存在线程同步增加 过滤调同步增加情况!");
} else {
System.out.println("ThradName(add)=" + ThradName + " =========== oldValue=" + oldValue
+ " newValue=" + newValue);
}
}
}
public void delete() {
Thread curThread = Thread.currentThread();
String ThradName = curThread.getName();
while (true) {
synchronized (this) {
while (value == 0) {
try {
// https://blog.csdn.net/syf1970/article/details/50965779
//notifyAll()同时也带来了弊端,它要唤醒所有的被等待的线程,意味着既唤醒了对方, 也唤醒了本方
notifyAll();
System.out.println("~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=" + ThradName +" wait() begin~~~~~~~");
wait();
System.out.println("~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=" + ThradName +" wait() end~~~~~~~");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
synchronized (this) {
if (value < VectorSize) {
System.out.println("##### ThradName(delete) " + ThradName +" value < 10 notifyAll() 通知生产者生产 begin #####");
notifyAll();
System.out.println("##### ThradName(delete) " + ThradName +" value < 10 notifyAll() 通知生产者生产 end #####");
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
int oldValue = 0;
int newValue = 0;
synchronized (deleteObjectLock) {
if (value > 0) {
oldValue = value;
value--;
newValue = value;
}
}
if (oldValue == 0 && newValue == 0) {
System.out.println("ThradName(delete)=" + ThradName + " 存在线程同步删除 过滤调同步删除情况!");
} else {
System.out.println("ThradName(delete)=" + ThradName + " =========== oldValue=" + oldValue
+ " newValue=" + newValue);
}
}
}
public class RunnableAdd implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
add();
}
}
public class RunnableDelete implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
delete();
}
}
}
/*
输出:
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() end~~~~~~~ 【notifiAll() 的 弊端】
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-5 wait() end~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-5 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() end~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-3 wait() end~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-3 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() end~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-5 wait() end~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-5 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() end~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-3 wait() end~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-3 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() end~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-5 wait() end~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-5 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() end~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-3 wait() end~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-3 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() end~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-5 wait() end~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-5 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() end~~~~~~~
##### ThradName(delete) Thread-4 value < 10 notifyAll() 通知生产者生产 begin #####
ThradName(add)=Thread-0 =========== oldValue=0 newValue=1
ThradName(add)=Thread-1 =========== oldValue=1 newValue=2
##### ThradName(delete) Thread-4 value < 10 notifyAll() 通知生产者生产 end #####
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-3 wait() end~~~~~~~
##### ThradName(delete) Thread-3 value < 10 notifyAll() 通知生产者生产 begin #####
*/
/*
使用 Lock 来替代 synchronized JDK新特性
*在多生产者多消费者问题中,我们通过while判断和notifyAll()全唤醒方法解决了问题,
* 【但是notifyAll()同时也带来了弊端,它要唤醒所有的被等待的线程】,【意味着既唤醒了对方,
* 也唤醒了本方】,在唤醒本方线程后还要不断判断标记,就降低了程序的效率。我们希望只唤醒对方的线程。
* Lock(接口)实现提供了比使用synchronized方法和语句可获得的更广泛的锁定操作。
* jdk1.5以后将同步和锁封装成了对象,并将操作锁的隐式方式定义到了该对象中,将隐式动作变成了显示动作
* ReentrantLock类是Lock类的子类,实现Lock接口
*
*
* 在jdk新特性中,用Lock来代替synchronized,用condition来代替监视器方法(wait()、notify()、notifyAll())。
interface Condition //Condition接口,替代Object类里的wait()、notify()、notifyAll()方法
{
await();
signal();
signalAll();
}
Lock lock=new ReectrantLock(); //一个锁上创建两个监视器,一个锁上就有多个监视器方法
Condition c1=lock.newCondition(); //每个监视器里都有await()、signal()、signalAll()方法
Condition c2=lock.newCondition();
*/
package test;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/*当操作线程的状态,如wait(),notify()等,如果没有给其加上同步方法,此时就会引起该异常。
* 加上synchronizied关键字,将其编程同步代码块或同步方法,该异常消失。
*
*
* synchronized (this) { wait()} 当线程执行到同步代码块中的 wait()时 本线程会阻塞,并且交出 synchronized 锁
* 当其他地方调用到 notify() 时会唤醒当前线程,但是如果还是得不到锁 那么当前线程仍然继续阻塞
* */
public class SyncAndWaitTest {
public static Object addObjectLock = new Object();
public static Object deleteObjectLock = new Object();
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition addCondition=lock.newCondition(); //add 生产者的监视器
Condition deleteCondition =lock.newCondition(); //delete 消费者的监视器
public volatile int value = 0;
public static int VectorSize = 10;
public static int AdderNumer = 3;
public static int DeleteNumer = 3;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("==============main begin===============");
SyncAndWaitTest obj = new SyncAndWaitTest();
for (int i = 0; i < AdderNumer; i++) {
new Thread(obj.new RunnableAdd()).start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < DeleteNumer; i++) {
new Thread(obj.new RunnableDelete()).start();
}
System.out.println("==============main end===============");
}
public void add() {
Thread curThread = Thread.currentThread();
String ThradName = curThread.getName();
while (true) {
lock.lock();
try{
while (value >= VectorSize) {
try {
deleteCondition.signalAll();
System.out.println("~~~~~~ThradName(add)=" + ThradName +" wait() begin~~~~~~~");
addCondition.await();
System.out.println("~~~~~~ThradName(add)=" + ThradName +" wait() end~~~~~~~");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
finally{
lock.unlock();
}
lock.lock();
try{
if (value >= 1) {
System.out.println("##### ThradName(add) " + ThradName +" value >= 1 notifyAll() 通知消费者消费 begin #####");
deleteCondition.signalAll();
System.out.println("##### ThradName(add) " + ThradName +" value >= 1 notifyAll() 通知消费者消费 end #####");
}}
finally{
lock.unlock();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
int oldValue = 0;
int newValue = 0;
synchronized (addObjectLock) {
if (value < VectorSize) {
oldValue = value;
value++;
newValue = value;
}
}
if (oldValue == 0 && newValue == 0) {
System.out.println("ThradName(add)=" + ThradName + " 存在线程同步增加 过滤调同步增加情况!");
} else {
System.out.println("ThradName(add)=" + ThradName + " =========== oldValue=" + oldValue
+ " newValue=" + newValue);
}
}
}
public void delete() {
Thread curThread = Thread.currentThread();
String ThradName = curThread.getName();
while (true) {
lock.lock();
try{
while (value == 0) {
try {
addCondition.signalAll();
System.out.println("~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=" + ThradName +" wait() begin~~~~~~~");
deleteCondition.await();
System.out.println("~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=" + ThradName +" wait() end~~~~~~~");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
finally{
lock.unlock();
}
lock.lock();
try {
if (value < VectorSize) {
System.out.println("##### ThradName(delete) " + ThradName +" value < 10 notifyAll() 通知生产者生产 begin #####");
deleteCondition.signalAll();
System.out.println("##### ThradName(delete) " + ThradName +" value < 10 notifyAll() 通知生产者生产 end #####");
}
}
finally{
lock.unlock();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
int oldValue = 0;
int newValue = 0;
synchronized (deleteObjectLock) {
if (value > 0) {
oldValue = value;
value--;
newValue = value;
}
}
if (oldValue == 0 && newValue == 0) {
System.out.println("ThradName(delete)=" + ThradName + " 存在线程同步删除 过滤调同步删除情况!");
} else {
System.out.println("ThradName(delete)=" + ThradName + " =========== oldValue=" + oldValue
+ " newValue=" + newValue);
}
}
}
public class RunnableAdd implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
add();
}
}
public class RunnableDelete implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
delete();
}
}
}
/*输出:
* ==============main begin===============
==============main end===============
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-3 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() begin~~~~~~~
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-5 wait() begin~~~~~~~
ThradName(add)=Thread-1 =========== oldValue=2 newValue=3
ThradName(add)=Thread-0 =========== oldValue=1 newValue=2
ThradName(add)=Thread-2 =========== oldValue=0 newValue=1
##### ThradName(add) Thread-1 value >= 1 notifyAll() 通知消费者消费 begin #####
##### ThradName(add) Thread-1 value >= 1 notifyAll() 通知消费者消费 end #####
##### ThradName(add) Thread-0 value >= 1 notifyAll() 通知消费者消费 begin #####
##### ThradName(add) Thread-0 value >= 1 notifyAll() 通知消费者消费 end #####
##### ThradName(add) Thread-2 value >= 1 notifyAll() 通知消费者消费 begin #####
##### ThradName(add) Thread-2 value >= 1 notifyAll() 通知消费者消费 end #####
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-3 wait() end~~~~~~~
##### ThradName(delete) Thread-3 value < 10 notifyAll() 通知生产者生产 begin #####
##### ThradName(delete) Thread-3 value < 10 notifyAll() 通知生产者生产 end #####
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-4 wait() end~~~~~~~
##### ThradName(delete) Thread-4 value < 10 notifyAll() 通知生产者生产 begin #####
##### ThradName(delete) Thread-4 value < 10 notifyAll() 通知生产者生产 end #####
~~~~~~ThradName(delete)=Thread-5 wait() end~~~~~~~
##### ThradName(delete) Thread-5 value < 10 notifyAll() 通知生产者生产 begin #####
##### ThradName(delete) Thread-5 value < 10 notifyAll() 通知生产者生产 end #####
ThradName(add)=Thread-2 =========== oldValue=3 newValue=4
*
*
*/
System.Property系统默认属性值
System.Property系统默认属性值
public class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (String key : System.getProperties().stringPropertyNames()) {
System.out.println("key:" + key + " value:" + System.getProperties().getProperty(key));
}
}
}
输出属性值如下:
key:java.runtime.name value:Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment
key:sun.boot.library.path value:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib
key:java.vm.version value:25.141-b15
key:gopherProxySet value:false
key:java.vm.vendor value:Oracle Corporation
key:java.vendor.url value:http://java.oracle.com/
key:path.separator value::
key:java.vm.name value:Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM
key:file.encoding.pkg value:sun.io
key:user.country value:CN
key:sun.java.launcher value:SUN_STANDARD
key:sun.os.patch.level value:unknown
key:java.vm.specification.name value:Java Virtual Machine Specification
key:user.dir value:/Users/aaa/IdeaProjects/Test
key:java.runtime.version value:1.8.0_141-b15
key:java.awt.graphicsenv value:sun.awt.CGraphicsEnvironment
key:java.endorsed.dirs value:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/endorsed
key:os.arch value:x86_64
key:java.io.tmpdir value:/var/folders/dn/g8yhcfnj3gnbj9421vfpb52c0000gn/T/
key:line.separator value:
key:java.vm.specification.vendor value:Oracle Corporation
key:os.name value:Mac OS X
key:sun.jnu.encoding value:UTF-8
key:java.library.path value:/Users/aaa/Library/Java/Extensions:/Library/Java/Extensions:/Network/Library/Java/Extensions:/System/Library/Java/Extensions:/usr/lib/java:.
key:jboss.modules.system.pkgs value:com.intellij.rt
key:java.specification.name value:Java Platform API Specification
key:java.class.version value:52.0
key:sun.management.compiler value:HotSpot 64-Bit Tiered Compilers
key:os.version value:10.12.6
key:http.nonProxyHosts value:local|*.local|169.254/16|*.169.254/16
key:user.home value:/Users/aaa
key:user.timezone value:
key:java.awt.printerjob value:sun.lwawt.macosx.CPrinterJob
key:file.encoding value:UTF-8
key:java.specification.version value:1.8
key:user.name value:aaa
key:java.class.path value:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/charsets.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/deploy.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/ext/cldrdata.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/ext/dnsns.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/ext/jaccess.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/ext/jfxrt.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/ext/localedata.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/ext/nashorn.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/ext/sunec.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/ext/sunjce_provider.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/ext/sunpkcs11.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/ext/zipfs.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/javaws.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/jce.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/jfr.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/jfxswt.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/jsse.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/management-agent.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/plugin.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/resources.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/rt.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/lib/ant-javafx.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/lib/dt.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/lib/javafx-mx.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/lib/jconsole.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/lib/packager.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/lib/sa-jdi.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/lib/tools.jar:/Users/aaa/IdeaProjects/Test/out/production/Test:/Applications/IntelliJ IDEA.app/Contents/lib/idea_rt.jar:/Users/aaa/Library/Caches/IntelliJIdea2018.2/captureAgent/debugger-agent.jar
key:java.vm.specification.version value:1.8
key:sun.arch.data.model value:64
key:java.home value:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre
key:sun.java.command value:A
key:java.specification.vendor value:Oracle Corporation
key:user.language value:zh
key:awt.toolkit value:sun.lwawt.macosx.LWCToolkit
key:java.vm.info value:mixed mode
key:java.version value:1.8.0_141
key:java.ext.dirs value:/Users/aaa/Library/Java/Extensions:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/ext:/Library/Java/Extensions:/Network/Library/Java/Extensions:/System/Library/Java/Extensions:/usr/lib/java
key:sun.boot.class.path value:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/resources.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/rt.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/sunrsasign.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/jsse.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/jce.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/charsets.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/jfr.jar:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_141.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/classes:/Users/aaa/Library/Caches/IntelliJIdea2018.2/captureAgent/debugger-agent-storage.jar
key:java.vendor value:Oracle Corporation
key:file.separator value:/
key:java.vendor.url.bug value:http://bugreport.sun.com/bugreport/
key:sun.cpu.endian value:little
key:sun.io.unicode.encoding value:UnicodeBig
key:socksNonProxyHosts value:local|*.local|169.254/16|*.169.254/16
key:ftp.nonProxyHosts value:local|*.local|169.254/16|*.169.254/16
key:sun.cpu.isalist value:
T
Top-level classes 和 Inner classes
Top-level classes: 指可以被声明为包成员,文件名字就是类名字的顶级文件。每一个top-level类对应于一个文件名与类名相同的java文件
因为top-level class已经是top-level,所以没必要声明为static。■ 如果把top-level class声明为static,编译器会报错。 接口java文件 声明为static 编译器会报错
■Inner classes: 内部类
在top-level class中可以定义inner class,根据inner class定义方式的不同,inner class可以有如下四种形式:
1.Anonymous匿名类 【因为匿名类没有标准的类声明,所以不可以声明为static】 匿名类没有static的说法
okButton.addActionListener( new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
dispose();
}
});
2. Local 局部类: 在函数中new 出来的类
就像局部变量一样,局部类不能声明为public,private,protected或static。
method(){
List list1 = new List();
}
3.Member 成员类:
成员类_内部类 是唯一可以声明为static类,当把成员类声明为static的时候,它就变成top-level class。成员类_内部类 没有被声明为static 那么它就是普通的 内部类_成员类
4. 静态内部类
输出结果:
======================Outter static block begin======================
Outter => static_byte_Outter_Init== 0x0f
Outter => static_byte_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== 0x00
Outter => static_boolean_Outter_Init== false
Outter => static_boolean_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== false
Outter => static_char_Outter_Init== a
Outter => static_char_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值==
Outter => static_short_Outter_Init== 1
Outter => static_short_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== 0
Outter => static_int_Outter_Init== 100
Outter => static_int_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== 0
Outter => static_long_Outter_Init== 10000
Outter => static_long_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== 0
Outter => static_float_Outter_Init== 3.1415
Outter => static_float_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== 0.0
Outter => static_double_Outter_Init== 3.1415926
Outter => static_double_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== 0.0
Outter => static_String_Outter_Init== Outter => static_String_Outter_Init
Outter => static_String_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== null
======================Outter static block end======================
############################Outter out =new Outter(); Begin ################################
======================Outter object block begin======================
Outter => byte_Outter_Init== 0x02
Outter => byte_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== 0x00
Outter => boolean_Outter_Init== true
Outter => boolean_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== false
Outter => char_Outter_Init== b
Outter => char_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值==
Outter => short_Outter_Init== 2
Outter => short_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== 0
Outter => int_Outter_Init== 200
Outter => int_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== 0
Outter => long_Outter_Init== 200000
Outter => long_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== 0
Outter => float_Outter_Init== 6.283
Outter => float_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== 0.0
Outter => double_Outter_Init== 6.28302945
Outter => double_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== 0.0
Outter => String_Outter_Init== Outter => String_Outter_Init
Outter => String_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== null
======================Outter object block end======================
=================== Outter 构造函数 Begin===================
=================== Outter 构造函数 End===================
############################Outter out =new Outter(); End ################################
############################Inner_Interface Implement Begin ################################
String_Inner_Interface
Inner_Interface => String_static_Inner_Interface
======================Inner_Interface_static_implementMethod begin======================
String_Inner_Interface
Inner_Interface => String_static_Inner_Interface
======================Inner_Interface_static_implementMethod end======================
############################Inner_Interface Implement End ################################
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@Inner_static_Object String Begin @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
======================Inner_static_Object static block begin======================
======================Inner_static_Object static block end======================
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@Inner_static_Object String ENd @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
#############Outter.Inner_static_Object.Inner_static_Object_static_method() BEGIN ################
======================Inner_static_Object_method begin======================
Inner_static_Object => String_static_Inner_static_Object <Inner_static_Object staic block>
======================Inner_static_Object_method end======================
#############Outter.Inner_static_Object.Inner_static_Object_static_method() END ################
############################new Inner_static_Object(); Begin ################################
======================Inner_static_Object object block begin======================
======================Inner_static_Object object block end======================
############################new Inner_static_Object(); End ################################
############################ mInner_static_Object.Inner_static_Object_method Begin ################################
======================Inner_Object_method begin======================
Inner_static_Object => String_static_Inner_static_Object <Inner_static_Object staic block> <Inner_static_Object object block>
Inner_static_Object => String_Inner_static_Object <Inner_static_Object object block>
======================Inner_Object_method end======================
############################ mInner_static_Object.Inner_static_Object_method End ################################
##############Outter.Inner_Object mInner_Object = out.new Inner_Object() Begin ###################
======================Inner_Object block begin======================
Inner_Object => String_static_Inner_Object
Inner_Object => String_Inner_Object
======================Inner_Object block end======================
Inner_Object => String_Inner_Object
Object方式访问非静态内部类静态成员: Inner_Object => String_static_Inner_Object
Class方式访问非静态内部类静态成员:a Inner_Object => String_static_Inner_Object
##############Outter.Inner_Object mInner_Object = out.new Inner_Object() END ###################
package test;
public class Outter {
// =================== Outter 构造函数 Begin===================
public Outter() {
System.out.println("=================== Outter 构造函数 Begin===================");
System.out.println("=================== Outter 构造函数 End===================");
}
// =================== Outter 构造函数 End===================
// =================== Propertys Begin===================
// byte boolean char short int long float double String
static byte static_byte_Outter_Init = 0x0F; // 声明时初始化的静态属性 byte
static byte static_byte_Outter_Default ; // 声明时就不初始化的静态属性 byte
byte byte_Outter_Init = 0x02; // 声明时初始化的对象属性 byte
byte byte_Outter_Default; // 声明时不初始化的对象属性 byte
static boolean static_boolean_Outter_Init = false; // 声明时初始化的静态属性 boolean
static boolean static_boolean_Outter_Default ; // 声明时就不初始化的静态属性 boolean
boolean boolean_Outter_Init = true; // 声明时初始化的对象属性 boolean
boolean boolean_Outter_Default; // 声明时不初始化的对象属性 boolean
static char static_char_Outter_Init ='a'; // 声明时初始化的静态属性 char
static char static_char_Outter_Default; // 声明时就不初始化的静态属性 char
char char_Outter_Init = 'b'; // 声明时初始化的对象属性 char
char char_Outter_Default; // 声明时不初始化的对象属性 char
static short static_short_Outter_Init = 1; // 声明时初始化的静态属性 short
static short static_short_Outter_Default; // 声明时就不初始化的静态属性 short
short short_Outter_Init = 2 ; // 声明时初始化的对象属性 short
short short_Outter_Default; // 声明时不初始化的对象属性 short
static int static_int_Outter_Init = 100; // 声明时初始化的静态属性 int
static int static_int_Outter_Default; // 声明时就不初始化的静态属性 int
int int_Outter_Init =200; // 声明时初始化的对象属性 int
int int_Outter_Default; // 声明时不初始化的对象属性 int
static long static_long_Outter_Init = 10000L; // 声明时初始化的静态属性 long
static long static_long_Outter_Default; // 声明时就不初始化的静态属性 long
long long_Outter_Init = 200000L; // 声明时初始化的对象属性 long
long long_Outter_Default; // 声明时不初始化的对象属性 long
static float static_float_Outter_Init = 3.1415F; // 声明时初始化的静态属性 float
static float static_float_Outter_Default; // 声明时就不初始化的静态属性 float
float float_Outter_Init = 6.2830F; // 声明时初始化的对象属性 float
float float_Outter_Default; // 声明时不初始化的对象属性 float
static double static_double_Outter_Init = 3.1415926D; // 声明时初始化的静态属性 double
static double static_double_Outter_Default; // 声明时就不初始化的静态属性 double
double double_Outter_Init = 6.28302945D; // 声明时初始化的对象属性 double
double double_Outter_Default; // 声明时不初始化的对象属性 double
static String static_String_Outter_Init = "Outter => static_String_Outter_Init "; // 声明时初始化的静态属性 String
static String static_String_Outter_Default; // 声明时就不初始化的静态属性 String
String String_Outter_Init ="Outter => String_Outter_Init "; // 声明时初始化的对象属性 String
String String_Outter_Default; // 声明时不初始化的对象属性 String
// =================== Propertys End===================
// ===================static Block Begin===================
static {
System.out.println("======================Outter static block begin======================");
System.out.println("Outter => static_byte_Outter_Init== "+byteToHex(static_byte_Outter_Init));
System.out.println("Outter => static_byte_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== "+byteToHex(static_byte_Outter_Default));
System.out.println("Outter => static_boolean_Outter_Init== "+static_boolean_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => static_boolean_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== "+static_boolean_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => static_char_Outter_Init== "+static_char_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => static_char_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== "+static_char_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => static_short_Outter_Init== "+static_short_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => static_short_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== "+static_short_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => static_int_Outter_Init== "+static_int_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => static_int_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== "+static_int_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => static_long_Outter_Init== "+static_long_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => static_long_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== "+static_long_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => static_float_Outter_Init== "+static_float_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => static_float_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== "+static_float_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => static_double_Outter_Init== "+static_double_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => static_double_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== "+static_double_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => static_String_Outter_Init== "+static_String_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => static_String_Outter_Default 静态属性初始化默认值== "+static_String_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("======================Outter static block end======================");
}
{
System.out.println("======================Outter object block begin======================");
System.out.println("Outter => byte_Outter_Init== "+ byteToHex(byte_Outter_Init));
System.out.println("Outter => byte_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== "+ byteToHex(byte_Outter_Default));
System.out.println("Outter => boolean_Outter_Init== "+ boolean_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => boolean_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== "+ boolean_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => char_Outter_Init== "+ char_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => char_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== "+ char_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => short_Outter_Init== "+ short_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => short_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== "+ short_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => int_Outter_Init== "+ int_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => int_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== "+ int_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => long_Outter_Init== "+ long_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => long_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== "+ long_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => float_Outter_Init== "+ float_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => float_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== "+ float_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => double_Outter_Init== "+ double_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => double_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== "+ double_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("Outter => String_Outter_Init== "+ String_Outter_Init);
System.out.println("Outter => String_Outter_Default 对象初始化默认值== "+ String_Outter_Default);
System.out.println("======================Outter object block end======================");
}
// =================== Block End===================
// =================== Inner Interface Begin===================
interface Inner_Interface{
static String String_static_Inner_Interface = "Inner_Interface => String_static_Inner_Interface";
String String_Inner_Interface = "String_Inner_Interface";
void Inner_Interface_method();
static void Inner_Interface_static_ImplementMethod() {
System.out.println("======================Inner_Interface_static_implementMethod begin======================");
System.out.println(String_Inner_Interface);
System.out.println(String_static_Inner_Interface);
System.out.println("======================Inner_Interface_static_implementMethod end======================");
}
}
// =================== Inner Interface End===================
// =================== Inner_static_Object Begin===================
static class Inner_static_Object{
static String String_static_Inner_static_Object = " Inner_static_Object => String_static_Inner_static_Object" ;
String String_Inner_static_Object = "Inner_static_Object => String_Inner_static_Object";
static {
System.out.println("======================Inner_static_Object static block begin======================");
String_static_Inner_static_Object = String_static_Inner_static_Object +" <Inner_static_Object staic block>";
System.out.println("======================Inner_static_Object static block end======================");
}
{
System.out.println("======================Inner_static_Object object block begin======================");
String_Inner_static_Object = String_Inner_static_Object +" <Inner_static_Object object block>";
String_static_Inner_static_Object = String_static_Inner_static_Object +" <Inner_static_Object object block>";
System.out.println("======================Inner_static_Object object block end======================");
}
static void Inner_static_Object_static_method(){
System.out.println("======================Inner_static_Object_method begin======================");
System.out.println(String_static_Inner_static_Object);
System.out.println("======================Inner_static_Object_method end======================");
}
void Inner_static_Object_method(){
System.out.println("======================Inner_Object_method begin======================");
System.out.println(String_static_Inner_static_Object);
System.out.println(String_Inner_static_Object);
System.out.println("======================Inner_Object_method end======================");
}
}
// =================== Inner_static_Object End===================
// =================== Inner_Object Begin===================
class Inner_Object{
final static String String_static_Inner_Object = " Inner_Object => String_static_Inner_Object" ;
String String_Inner_Object = "Inner_Object => String_Inner_Object";
{
System.out.println("======================Inner_Object block begin======================");
System.out.println(String_static_Inner_Object);
System.out.println(String_Inner_Object);
System.out.println("======================Inner_Object block end======================");
}
void Inner_Object_method(){
System.out.println("======================Inner_Object_method begin======================");
System.out.println(String_static_Inner_Object);
System.out.println(String_Inner_Object);
System.out.println("======================Inner_Object_method end======================");
}
}
// =================== Inner_Object End===================
final static char[] hexArray = "0123456789ABCDEF".toCharArray();
public static String bytesToHex(byte[] bytes) {
char[] hexChars = new char[bytes.length * 2];
for ( int j = 0; j < bytes.length; j++ ) {
int v = bytes[j] & 0xFF;
hexChars[j * 2] = hexArray[v >>> 4];
hexChars[j * 2 + 1] = hexArray[v & 0x0F];
}
return new String(hexChars);
}
public static String byteToHex(byte byteValue) {
return byteValue > 0x0f || byteValue < 0x00 ? "0x"+Integer.toHexString(byteValue & 0xff ) : "0x0"+Integer.toHexString(byteValue & 0xff);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("############################Outter out =new Outter(); Begin ################################");
Outter out =new Outter();
System.out.println("############################Outter out =new Outter(); End ################################");
System.out.println("############################Inner_Interface Implement Begin ################################");
Inner_Interface interfaceObj = new Inner_Interface(){
@Override
public void Inner_Interface_method() {
}
};
System.out.println(interfaceObj.String_Inner_Interface);
System.out.println(interfaceObj.String_static_Inner_Interface);
Inner_Interface.Inner_Interface_static_ImplementMethod();
System.out.println("############################Inner_Interface Implement End ################################");
// 当第一次 调用 内部静态类的静态代码 静态属性时候 会触发 static{} 代码块的执行
// 静态代码块 只会执行一次
System.out.println("@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@Inner_static_Object String Begin @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@");
String str = Outter.Inner_static_Object.String_static_Inner_static_Object;
System.out.println("@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@Inner_static_Object String ENd @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@");
System.out.println("#############Outter.Inner_static_Object.Inner_static_Object_static_method() BEGIN ################");
Outter.Inner_static_Object.Inner_static_Object_static_method();
System.out.println("#############Outter.Inner_static_Object.Inner_static_Object_static_method() END ################");
System.out.println("############################new Inner_static_Object(); Begin ################################");
Outter.Inner_static_Object mInner_static_Object = new Inner_static_Object();
System.out.println("############################new Inner_static_Object(); End ################################");
System.out.println("############################ mInner_static_Object.Inner_static_Object_method Begin ################################");
mInner_static_Object.Inner_static_Object_method();
System.out.println("############################ mInner_static_Object.Inner_static_Object_method End ################################");
System.out.println("##############Outter.Inner_Object mInner_Object = out.new Inner_Object() Begin ###################");
// 创建内部非静态类
Outter.Inner_Object mInner_Object = out.new Inner_Object();
System.out.println(mInner_Object.String_Inner_Object);
System.out.println("Object方式访问非静态内部类静态成员:"+mInner_Object.String_static_Inner_Object);
System.out.println("Class方式访问非静态内部类静态成员:a"+Outter.Inner_Object.String_static_Inner_Object);
System.out.println("##############Outter.Inner_Object mInner_Object = out.new Inner_Object() END ###################");
}
}
// java byte b = 0x80;为什么会报错 ?
// 因为什么0x 开头的是16进制,编译的时候会自动转成整数,而这个整数超过了byte的长度(byte取值范围是-128 ~ 127),
// 而0x80转为十进制 = 128所以报损失精度了,编译不过的
// 当第一次 调用 内部静态类的静态代码 静态属性时候 会触发 static{} 代码块的执行
// 静态代码块 只会执行一次
Top-level Class’s InnerClass 静态内部类相互继承 包含同名同方法的案例
静态内部类继承关系
User extends Person
User 和 Person 有相同的属性 那么 User的属性会替换Person的属性 在Person中 其实会调用到 User的属性
■ User的对象属性 的初始化阶段 【 相当于 {} Object Block】 在父类构造器完成之后,在自身构造器完成之前
public class OutterObject {
static class Person {
String name = "Person";
int age = 26;
{
System.out.println("===============Person.Block Begin ===============");
System.out.println("===============Person.Block END ===============");
}
public Person() {
System.out.println("===============Person() begin===============");
init();
System.out.println("===============Person() end===============");
}
protected void init() {
System.out.println("===============Person.init() begin===============");
System.out.println("Person.name:" + name + " Person.age:" + age);
System.out.println("===============Person.init() end===============");
}
}
static class User extends Person {
String name = "User";
int age = 27;
{
System.out.println("===============User.Block Begin ===============");
System.out.println("===============User.Block END ===============");
}
public User() { //【 User() 构造器默认是首先调用 super() 所以不管有没有写super() 效果都是一样的 】
System.out.println("===============User() Begin ===============");
init();
System.out.println("===============User() End ===============");
}
protected void init() {
System.out.println("===============User() init Begin===============");
super.init();
System.out.println("User.name:" + name + " User.age:" + age);
System.out.println("===============User() init END===============");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User();
}
}
输出:
===============Person.Block Begin =============== 【1. 父类的对象属性会被最先初始化 如果有静态属性那么会先初始化静态属性】
===============Person.Block END ===============
===============Person() begin=============== 【2. 父类的构造器开始执行 由于存在方法的重写 】 父类和子类同名同参数的方法
===============User() init Begin=============== 【3. 父类调用子类重写的方法】
===============Person.init() begin=============== 【4. 通过 super().init() 显示的调用父类的 init 方法】
Person.name:Person Person.age:26 【5. 父类的对象属性已经首先初始化了 所以能打印出父类初始化的值】
===============Person.init() end=============== 【父类的 init函数完成】
User.name:null User.age:0 【6. 返回到super().init()的下一条语句 由于Person父类的构造器还没完成 所以 子类的属性都是为空的 打印空 】
===============User() init END===============
===============Person() end=============== 【父类的构造器完成】
===============User.Block Begin =============== 【子类的 Block块 初始化操作开始】
===============User.Block END ===============
===============User() Begin =============== 【子类的构造器开始】
===============User() init Begin=============== 【7. User 构造器中的 init() 代码开始执行 方法】
===============Person.init() begin===============
Person.name:Person Person.age:26 【8. User的init()方法 通过 super.init() 现实的调用父类的 init()方法 再一次执行父类的属性的打印】
===============Person.init() end===============
User.name:User User.age:27 【9. 通过 System.out.println("User.name:" + name + " User.age:" + age); 打印出自己的属性】
===============User() init END===============
===============User() End ===============
多态存在的三个必要条件:要有继承、要有重写、父类变量引用子类对象。
方法覆盖重写要求参数列表必须一致,而方法重载要求参数列表必须不一致。
通过子类的引用访问同名方法时,默认是重写之后的同名方法。如果还要访问父类的同名方法,可以【使用super关键字来显示调用】。
访问
结论 :
1.父类与子类定义同名的变量,并不会覆盖,而是各自还有自己的空间,即使变量名相同
2.相同方法的情况下 父类方法调用的是子类重载的方法
Thread 和 Runnable的关系
1. 线程实现了 Runnable接口 线程的优先级 数值越大 优先级越大
public class Thread implements Runnable {
public static final int MIN_PRIORITY = 1;
public static final int NORM_PRIORITY = 5;
public static final int MAX_PRIORITY = 10;
}
2. 接口内定义了 run()方法
public interface Runnable {
void run();
}
3. 外界通过 start() 方法最终调用到 run() 方法 内 执行自定义代码
public synchronized void start() {
}
4. sleep() 是Thrad类的静态方法 不是Object的方法 区别于 object的 wait() 方法
public static void sleep(long time) throws InterruptedException {
}
5.Thread.yield()方法作用是:暂停当前正在执行的线程对象(及放弃当前拥有的cup资源),并执行其他线程
yield()做的是让当前运行线程回到可运行状态 【正在运行状态 --> 可运行状态】,以允许具有相同优先级的其他线程获得运行机会。
public static void yield() {
}
使用yield()的目的:
是让相同优先级的线程之间能适当的轮转执行
但是,实际中无法保证yield()达到让步目的,因为让步的线程还有可能被线程调度程序再次选中
结论:yield()从未导致线程转到等待/睡眠/阻塞状态。在大多数情况下,yield()将导致线程从运行状态转到可运行状态,但有可能没有效果
6. Thread.join() 方法
join() 方法的作用是调用线程等待该线程完成后,才能继续用下运行
可实现 线程的循序执行
但是 此方法有重大的性能缺陷,能将多线程程序变成单线程程序,执行时间瞬间翻倍
7. 实例 new Thread( new ThreadChild())
package test;
public class ThreadObj extends Thread{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadObj mThreadObj = new ThreadObj();
// 以Thread父类 ThreadObj 为参数 构建 Thread , 实际执行的方法是 public Thread(Runnable runnable) {} 构造函数
// 把 Thread父类 ThreadObj 当做一个 Runnable 接口的实例 去创建 Thread ,因为 public class Thread implements Runnable ,Thrad定义时就已经实现Runnable方法
Thread thrad = new Thread(mThreadObj);
thrad.start();
}
public void run(){ // 子类重写的 run() 方法 重写是 面向对象特征之一 实现多态
for(int i =0 ; i <3 ; i++)
System.out.println(i+"..");
}
}
Thread的顺序执行:join 以及 CyclicBarrier Java线程同步工具类
join()方法的作用是调用线程等待该线程完成后,才能继续用下运行。
可以在主线程 调用 thread.join() 那么主线程会在 thread执行结束之后才会执行
但是 此方法有重大的性能缺陷,能将多线程程序变成单线程程序,执行时间瞬间翻倍
https://blog.csdn.net/yin380697242/article/details/53313622
CyclicBarrier 是一个同步工具类,它允许一组线程在到达某个栅栏点(common barrier point)互相等待,发生阻塞,直到最后一个线程到达栅栏点,栅栏才会打开,处于阻塞状态的线程恢复继续执行.
CountDownLatch 是一个线程同步工具 用于在main线程 等待所有 CountDownLatch 清空为0 后 才继续执行 与join() 方法类似 不过 CountDownLatch 用于多个线程 join只能用于一个线程
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class ThreadOrderTest {
static int intValue = 0;
static ArrayList<ThreadOrder> list = new ArrayList<ThreadOrder>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ThreadOrder curThread = new ThreadOrder();
list.add(curThread);
}
int size = list.size();
System.out.println("list.size: " + size);
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
list.get(i).setPreThread(list.get(i - 1));
}
for (ThreadOrder therad : list) {
therad.start();
}
}
public static class ThreadOrder extends Thread {
public Thread preThread;
public ThreadOrder() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Thread getPreThread() {
return preThread;
}
public void setPreThread(Thread preThread) {
this.preThread = preThread;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (preThread != null) {
try {
preThread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
intValue++;
Thread curThread = Thread.currentThread();
String ThradName = curThread.getName();
System.out.println("ThradName=" + ThradName + " intValue=" + intValue);
}
}
}
Time时间复杂度 和 空间复杂度
时间复杂度: 关系函数 T(n)=O(f(n)) 我们研究当N 不断增大时 T与N的关系映射
时间复杂度就是问题规模N对时间的映射T. O只是去掉杂项
1. 常数级别
T(n) = O(1) = C; 表示当 常数级别的运算时,N的值不断增大 T的花费时间变化很小 如图 常数级别
T = O(N + 100);
2.对数级别
T(n) = O(Log N) = C LogN; 表示当 常数级别的运算时,N的值不断增大 T的花费时间变化很小 比常熟级别大 如图
T = O(log N );
3. 线性级别:
T(n) = O( N) = C N; 时间复杂度如图
T = O( 10 * N )
4. 线性对数级别
T(n) = O( N * log N ) = C N loh N; 时间复杂度如图
T = O( 10 * log N )
5.平方级别
T(n) = O(n²) = Cn² : 表示当n很大 持续增大 的时候,复杂度约等于Cn²,C是某个常数,简单说就是当n足够大的时候,n的线性增长,复杂度将沿平方增长。
T = O( N * N ) 时间复杂度如图
1+2+3+4+……+n =(1+n)*n/2 = O(n²) = Cn² 的复杂度
6.立方级别
T = O( N * N * N) =CN^3 时间复杂度如图 N变动幅度小 T变动幅度大
7.指数级别
T(n) = O(2^n) = Cn² : 时间复杂度最高
T = O( 2 ^ N )
当评价一个算法的时间复杂度时: 就是从 以下七个复杂度回答一个对应的代码类型的复杂度 如上图示例代码
1.常数级别 O(1) = C;
2.对数级别 O(Log N) = C LogN;
3.线性级别 O(N) = C N;
4.线性对数级别 O(N*logN) = C N*log N;
5.平方级别 O(n²) = Cn² ; 1+2+3+4+……+n =(1+n)*n/2 = O(n²) = Cn² 的复杂度
6.立方级别 O( n³) =Cn³ ;
7.指数级别 O(2ⁿ) = C2ⁿ ;
ThreadLocal 对象
(ThreadLocal_CSDN)[https://www.cnblogs.com/qilong853/p/5982878.html]
ThreadLocal的使用不是为了能让多个线程共同使用某一对象,而是我有一个线程A,其中我需要用到某个对象o,
这个对象o在这个线程A之内会被多处调用,而我不希望将这个对象o当作参数在多个方法之间传递,
于是,我将这个对象o放到TheadLocal中,这样,在这个线程A之内的任何地方,只要线程A之中的方法不修改这个对象o,
我都能取到同样的这个变量o。
ThreadPoolExecutor
Java 线程池-简书 ThreadPoolExecutor 线程池
《阿里巴巴java开发手册》
线程池不使用 Executors 去创建,而是通过 ThreadPoolExecutor 的方式,这样 的处理方式让写的同学更加明确线程池的运行规则,规避资源耗尽的风险。
说明: Executors 返回的线程池对象的弊端如下:会引起OOM危险
FixedThreadPool 和 SingleThreadPool : 允许的请求队列长度为 Integer.MAX_VALUE ,可能会堆积大量的请求,从而导致 OOM 。
CachedThreadPool 和 ScheduledThreadPool : 允许的创建线程数量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE ,可能会创建大量的线程,从而导致 OOM 。
实测例子:
TestCallable.class
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
//TestCallable.java
public class TestCallable implements Callable<String> {
private String name;
public TestCallable(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("#############" + this.name + " call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin " + "#############");
System.out.println("#############" + this.name + " call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End " + "#############");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return this.name;
}
}
ThreadPoolExecutorTest.class
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorCompletionService;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
//test.java
class ThreadPoolExecutorTest {
volatile int finishState = 0;
volatile Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutorTest pool = new ThreadPoolExecutorTest();
try {
pool.test4();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void test4() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
//java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.ThreadPoolExecutor
//(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit,
//BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue)
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 6, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(4));
threadPoolExecutor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true); // 允许核心线程超时退出
ExecutorCompletionService<String> executorCompletionService = new ExecutorCompletionService(threadPoolExecutor);
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("=================== Task join Begin ===================");
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
String name = "name_" + i;
TestCallable testCallable = new TestCallable(name);
try {
executorCompletionService.submit(testCallable);
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("---------------- Task 【" + i + " 】 Begin----------------");
System.out.println("++++++ 添加任务 name: " + name);
System.out.println("获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: " + threadPoolExecutor.getActiveCount());
System.out.println("线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: " + threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: " + threadPoolExecutor.getQueue().size());
System.out.println("当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: " + threadPoolExecutor.getTaskCount());
System.out.println("---------------- Task 【" + i + " 】 End----------------");
}
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("拒绝:" + name);
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
finishState = 1;
System.out.println("=================== Task join End ===================");
}
};
Thread addThread = new Thread(runnable);
addThread.start();
// System.out.println(" taskCount: " +
// threadPoolExecutor.getTaskCount());
// 添加的任务有被抛弃的。taskCount不一定等于添加的任务。
int completeCount = 0;
while (!(completeCount == threadPoolExecutor.getTaskCount() && finishState == 1)) {
Future<String> take = executorCompletionService.take();
String taskName = take.get();
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println(" *********** 任务: " + taskName + " 完成 Begin ***********");
System.out.println("---完成任务 name: " + taskName);
System.out.println("完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: " + threadPoolExecutor.getActiveCount());
System.out.println("线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: " + threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: " + threadPoolExecutor.getQueue().size());
System.out.println("线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): " + threadPoolExecutor.getTaskCount());
System.out.println("线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:" + (++completeCount));
System.out.println(" *********** 任务: " + taskName + " 完成 End ***********");
}
}
addThread.join(); // 主mian 线程 等待 addThred线程 执行结束 才继续执行
while (threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize() > 0) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
synchronized (lock) {
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
System.out.print(simpleDateFormat.format(new Date()));
System.out.print("Threadname: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.print(" ActiveCount: " + threadPoolExecutor.getActiveCount());
System.out.print(" poolSize: " + threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize());
System.out.print(" queueSize: " + threadPoolExecutor.getQueue().size());
System.out.println(" taskCount: " + threadPoolExecutor.getTaskCount());
}
}
// Tell threads to finish off. 终止线程池
// shutdown() 将线程池状态转为SHUTDOWN 并且拒绝新Task加入 中断所有空闲线程
// 正执行的线程需要运行结束才中断 WorkQueue中的任务还是会被线程执行
// threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
// shutdownNow() 将线程池状态转为STOP 并且拒绝新Task加入 中断所有的线程 正在执行的线程抛出异常后退出
// WorkQueue中的所有任务被抛弃 置空
threadPoolExecutor.shutdownNow();
// Wait for everything to finish.
// awaitTermination() 当前线程阻塞,直到
// 所有已提交的任务(包括正在跑的和队列中等待的)执行完 或者 或者等超时时间到 或者线程被中断,抛出InterruptedException
// 返回true(shutdown请求后所有任务执行完毕)或false(已超时)
while (!threadPoolExecutor.awaitTermination(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
System.out.println("complete");
}
System.out.println(" ~~~~~~~~~~~~ main thread end ~~~~~~~~~~~~");
}
}
输出结果:
=================== Task join Begin ===================
---------------- Task 【0 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_0
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 1
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 1
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 0
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 1
---------------- Task 【0 】 End----------------
---------------- Task 【1 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_1
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 2
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 2
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 0
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 2
---------------- Task 【1 】 End----------------
---------------- Task 【2 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_2
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 3
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 3
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 0
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 3
---------------- Task 【2 】 End----------------
---------------- Task 【3 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_3
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 3
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 3
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 1
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 4
---------------- Task 【3 】 End----------------
---------------- Task 【4 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_4
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 3
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 3
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 2
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 5
---------------- Task 【4 】 End----------------
---------------- Task 【5 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_5
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 3
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 3
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 3
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 6
---------------- Task 【5 】 End----------------
---------------- Task 【6 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_6
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 3
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 3
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 4
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 7
---------------- Task 【6 】 End----------------
---------------- Task 【7 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_7
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 4
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 4
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 4
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 8
---------------- Task 【7 】 End----------------
---------------- Task 【8 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_8
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 5
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 5
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 4
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 9
---------------- Task 【8 】 End----------------
---------------- Task 【9 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_9
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 4
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 10
---------------- Task 【9 】 End----------------
#############name_0 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_0 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_0 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_0
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 3
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 10
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:1
*********** 任务: name_0 完成 End ***********
---------------- Task 【10 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_10
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 4
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 11
---------------- Task 【10 】 End----------------
#############name_1 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_1 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_1 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_1
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 3
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 11
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:2
*********** 任务: name_1 完成 End ***********
---------------- Task 【11 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_11
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 4
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 12
---------------- Task 【11 】 End----------------
#############name_2 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_2 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_2 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_2
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 3
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 12
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:3
*********** 任务: name_2 完成 End ***********
---------------- Task 【12 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_12
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 4
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 13
---------------- Task 【12 】 End----------------
拒绝:name_13
拒绝:name_14
拒绝:name_15
拒绝:name_16
#############name_7 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_7 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_7 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_7
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 3
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 13
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:4
*********** 任务: name_7 完成 End ***********
---------------- Task 【17 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_17
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 4
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 14
---------------- Task 【17 】 End----------------
#############name_8 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_8 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_8 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_8
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 3
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 14
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:5
*********** 任务: name_8 完成 End ***********
---------------- Task 【18 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_18
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 4
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 15
---------------- Task 【18 】 End----------------
#############name_9 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_9 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_9 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_9
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 3
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 15
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:6
*********** 任务: name_9 完成 End ***********
---------------- Task 【19 】 Begin----------------
++++++ 添加任务 name: name_19
获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
阻塞队列中待执行任务数量 queueSize: 4
当前执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ) taskCount: 16
---------------- Task 【19 】 End----------------
#############name_3 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_3 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_3 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_3
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 3
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 16
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:7
*********** 任务: name_3 完成 End ***********
=================== Task join End ===================
#############name_4 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_4 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_4 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_4
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 2
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 16
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:8
*********** 任务: name_4 完成 End ***********
#############name_5 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_5 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_5 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_5
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 1
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 16
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:9
*********** 任务: name_5 完成 End ***********
#############name_6 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_6 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_6 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_6
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 6
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 0
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 16
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:10
*********** 任务: name_6 完成 End ***********
#############name_10 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_10 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_10 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_10
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 5
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 0
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 16
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:11
*********** 任务: name_10 完成 End ***********
#############name_11 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_11 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_11 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_11
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 4
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 0
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 16
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:12
*********** 任务: name_11 完成 End ***********
#############name_12 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_12 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_12 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_12
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 3
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 0
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 16
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:13
*********** 任务: name_12 完成 End ***********
#############name_17 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_17 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_17 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_17
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 2
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 0
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 16
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:14
*********** 任务: name_17 完成 End ***********
#############name_18 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_18 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_18 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_18
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 1
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 0
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 16
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:15
*********** 任务: name_18 完成 End ***********
#############name_19 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 Begin #############
#############name_19 call() 请求逻辑返回数据 End #############
*********** 任务: name_19 完成 Begin ***********
---完成任务 name: name_19
完成任务后 获取线程池活动线程数量 ActiveCount: 0
线程池线程数量总数(核心线程+非核心线程) poolSize: 6
完成任务后 阻塞队列中待执行任务数 queueSize: 0
线程池 执行的任务总量( 排除被抛弃任务 ): 16
线程池 已完成的任务(抛去因阻塞超长度而被抛弃的任务) finishTask:16
*********** 任务: name_19 完成 End ***********
07:56:06Threadname: main ActiveCount: 0 poolSize: 6 queueSize: 0 taskCount: 16
07:56:07Threadname: main ActiveCount: 0 poolSize: 6 queueSize: 0 taskCount: 16
07:56:08Threadname: main ActiveCount: 0 poolSize: 6 queueSize: 0 taskCount: 16
07:56:09Threadname: main ActiveCount: 0 poolSize: 1 queueSize: 0 taskCount: 16
07:56:10Threadname: main ActiveCount: 0 poolSize: 0 queueSize: 0 taskCount: 16
~~~~~~~~~~~~ main thread end ~~~~~~~~~~~~
U
V
W
X
XML中 @、@android:type、@*android:type、?、@+含义和区别
【@】: @代表引用资源
1.引用自定义资源。格式:@[package:]type/name
android:text="@string/hello"
2.引用系统资源。格式:@android:type/name
android:textColor="@android:color/opaque_red"
{ 其实@android:type/name是@[package:]type/name 的一个子类 }
type 包括: attr , id , style , string , dimen , integer , array , drawable , layout , interpolator , mipmap , transition
@android:attr/theme 属性类型
【@* 】: @* @*代表引用系统的非public资源。格式:@*android:type/name
格式:@*android:type/name
■系统资源定义分public和非public 。 public的声明在: <sdk_path>\platforms\android-8\data\res\values\public.xml 【文件 简略在底部】
@*android:type/name:可以调用系统定义的所有资源
@android:type/name:只能够调用publi属性的资源。
【? 】: ?问号代表引用主题属性
View中的某些属性 允许你引用当前主题定义属性的值
这个属性值只能在style资源和XML属性中使用 用于修饰View
它允许你通过将它们改变为当前主题提供的标准变化来改变UI元素的外观,■ 而不是提供具体的值 依据当前主题的对应属性决定UI的对应属性
android:textColor="?android:textDisabledColor"
【这和资源引用非常类似,除了我们使用一个"?"前缀代替了"@" 】
【@+ 】: @+代表在创建或引用资源 。格式:@+type/name
”+” 表示在R.java中名为type的内部类中添加一条记录。如"@+id/button"的含义是在R.java 文件中的id 这个静态内部类添加一条常量名为button
该常量就是该资源的标识符。如果标示符(包括系统资源)已经存在则表示引用该标示符。最常用的就是在定义资源ID中
@+id/资源ID名 新建一个资源ID
@id/资源ID名 应用现有已定义的资源ID,包括系统ID
@android:id/资源ID名 引用系统ID,其等效于@id/资源ID名
android:id="@+id/selectdlg"
android:id="@android:id/text1"
android:id="@id/button3"
Android\sdk\platforms\android-26\data\res\values\public.xml 大致内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<eat-comment />
<!-- type="attr" Begin -->
<public type="attr" name="theme" id="0x01010000" />
<public type="attr" name="label" id="0x01010001" />
<public type="attr" name="icon" id="0x01010002" />
<public type="attr" name="name" id="0x01010003" />
<public type="attr" name="manageSpaceActivity" id="0x01010004" />
<public type="attr" name="allowClearUserData" id="0x01010005" />
<public type="attr" name="permission" id="0x01010006" />
<public type="attr" name="readPermission" id="0x01010007" />
<public type="attr" name="writePermission" id="0x01010008" />
<public type="attr" name="protectionLevel" id="0x01010009" />
<public type="attr" name="permissionGroup" id="0x0101000a" />
...............
<!-- type="attr" End -->
<!-- type="id" Begin -->
<public type="id" name="background" id="0x01020000" />
<public type="id" name="checkbox" id="0x01020001" />
<public type="id" name="content" id="0x01020002" />
<public type="id" name="edit" id="0x01020003" />
<public type="id" name="empty" id="0x01020004" />
<public type="id" name="hint" id="0x01020005" />
<public type="id" name="icon" id="0x01020006" />
<public type="id" name="icon1" id="0x01020007" />
<public type="id" name="icon2" id="0x01020008" />
<public type="id" name="input" id="0x01020009" />
<public type="id" name="list" id="0x0102000a" />
<public type="id" name="message" id="0x0102000b" />
<public type="id" name="primary" id="0x0102000c" />
<public type="id" name="progress" id="0x0102000d" />
<public type="id" name="selectedIcon" id="0x0102000e" />
<public type="id" name="secondaryProgress" id="0x0102000f" />
<public type="id" name="summary" id="0x01020010" />
<public type="id" name="tabcontent" id="0x01020011" />
<public type="id" name="tabhost" id="0x01020012" />
<public type="id" name="tabs" id="0x01020013" />
<public type="id" name="text1" id="0x01020014" />
<public type="id" name="text2" id="0x01020015" />
<public type="id" name="title" id="0x01020016" />
<public type="id" name="toggle" id="0x01020017" />
<public type="id" name="widget_frame" id="0x01020018" />
<public type="id" name="button1" id="0x01020019" />
<public type="id" name="button2" id="0x0102001a" />
<public type="id" name="button3" id="0x0102001b" />
<!-- type="id" End -->
<!-- type="style" Begin -->
<public type="style" name="Animation" id="0x01030000" />
<public type="style" name="Animation.Activity" id="0x01030001" />
<public type="style" name="Animation.Dialog" id="0x01030002" />
<public type="style" name="Animation.Translucent" id="0x01030003" />
<public type="style" name="Animation.Toast" id="0x01030004" />
<public type="style" name="Theme" id="0x01030005" />
<public type="style" name="Theme.NoTitleBar" id="0x01030006" />
<public type="style" name="Theme.NoTitleBar.Fullscreen" id="0x01030007" />
<public type="style" name="Theme.Black" id="0x01030008" />
<public type="style" name="Theme.Black.NoTitleBar" id="0x01030009" />
<public type="style" name="Theme.Black.NoTitleBar.Fullscreen" id="0x0103000a" />
<!-- type="style" End -->
<!-- type="string" Begin -->
<public type="string" name="cancel" id="0x01040000" />
<public type="string" name="copy" id="0x01040001" />
<public type="string" name="copyUrl" id="0x01040002" />
<public type="string" name="cut" id="0x01040003" />
<public type="string" name="defaultVoiceMailAlphaTag" id="0x01040004" />
<public type="string" name="defaultMsisdnAlphaTag" id="0x01040005" />
<public type="string" name="emptyPhoneNumber" id="0x01040006" />
<public type="string" name="httpErrorBadUrl" id="0x01040007" />
<public type="string" name="httpErrorUnsupportedScheme" id="0x01040008" />
<public type="string" name="no" id="0x01040009" />
<public type="string" name="ok" id="0x0104000a" />
<public type="string" name="paste" id="0x0104000b" />
<public type="string" name="search_go" id="0x0104000c" />
<public type="string" name="selectAll" id="0x0104000d"
<!-- type="string" End -->
<!-- type="dimen" Begin -->
<public type="dimen" name="app_icon_size" id="0x01050000" />
<public type="dimen" name="thumbnail_height" id="0x01050001" />
<public type="dimen" name="thumbnail_width" id="0x01050002" />
<!-- type="dimen" End -->
<!-- type="color" Begin -->
<public type="color" name="white" id="0x0106000b" />
<public type="color" name="black" id="0x0106000c" />
<public type="color" name="transparent" id="0x0106000d" />
<public type="color" name="background_dark" id="0x0106000e" />
<public type="color" name="background_light" id="0x0106000f" />
<!-- type="color" End -->
<!-- type="array" Begin -->
<public type="array" name="emailAddressTypes" id="0x01070000" />
<public type="array" name="imProtocols" id="0x01070001" />
<public type="array" name="organizationTypes" id="0x01070002" />
<public type="array" name="phoneTypes" id="0x01070003" />
<public type="array" name="postalAddressTypes" id="0x01070004" />
<!-- type="array" End -->
<!-- type="drawable" Begin -->
<public type="drawable" name="alert_dark_frame" id="0x01080000" />
<public type="drawable" name="alert_light_frame" id="0x01080001" />
<public type="drawable" name="arrow_down_float" id="0x01080002" />
<public type="drawable" name="arrow_up_float" id="0x01080003" />
<public type="drawable" name="btn_default" id="0x01080004" />
<public type="drawable" name="btn_default_small" id="0x01080005" /
<!-- type="drawable" End -->
<!-- type="layout" Begin -->
<public type="layout" name="activity_list_item" id="0x01090000" />
<public type="layout" name="expandable_list_content" id="0x01090001" />
<public type="layout" name="preference_category" id="0x01090002" />
<public type="layout" name="simple_list_item_1" id="0x01090003" />
<public type="layout" name="simple_list_item_2" id="0x01090004" />
<public type="layout" name="simple_list_item_checked" id="0x01090005" />
<public type="layout" name="simple_expandable_list_item_1" id="0x01090006" />
<public type="layout" name="simple_expandable_list_item_2" id="0x01090007" />
<public type="layout" name="simple_spinner_item" id="0x01090008" />
<public type="layout" name="simple_spinner_dropdown_item" id="0x01090009" />
<public type="layout" name="simple_dropdown_item_1line" id="0x0109000a" />
<public type="layout" name="simple_gallery_item" id="0x0109000b" />
<public type="layout" name="test_list_item" id="0x0109000c" />
<public type="layout" name="two_line_list_item" id="0x0109000d" />
<public type="layout" name="browser_link_context_header" id="0x0109000e" />
<public type="layout" name="simple_list_item_single_choice" id="0x0109000f" />
<public type="layout" name="simple_list_item_multiple_choice" id="0x01090010" />
<public type="layout" name="select_dialog_item" id="0x01090011" />
<public type="layout" name="select_dialog_singlechoice" id="0x01090012" />
<public type="layout" name="select_dialog_multichoice" id="0x01090013" />
<!-- type="layout" End -->
<!-- type="anim" Begin -->
<public type="anim" name="fade_in" id="0x010a0000" />
<public type="anim" name="fade_out" id="0x010a0001" />
<public type="anim" name="slide_in_left" id="0x010a0002" />
<public type="anim" name="slide_out_right" id="0x010a0003" />
<public type="anim" name="accelerate_decelerate_interpolator" id="0x010a0004" />
<!-- type="anim" End -->
<!-- type="integer" Begin -->
<public type="integer" name="config_shortAnimTime" id="0x010e0000" />
<public type="integer" name="config_mediumAnimTime" id="0x010e0001" />
<public type="integer" name="config_longAnimTime" id="0x010e0002" />
<!-- type="integer" End -->
<!-- type="interpolator" Begin -->
<public type="interpolator" name="decelerate_quad" id="0x010c0001" />
<public type="interpolator" name="accelerate_cubic" id="0x010c0002" />
<public type="interpolator" name="decelerate_cubic" id="0x010c0003" />
<!-- type="interpolator" End -->
<!-- type="mipmap" Begin -->
<public type="mipmap" name="sym_def_app_icon" id="0x010d0000" /> 【 默认APP 应用图标 】
<!-- type="mipmap" End -->
<!-- type="transition" Begin -->
<public type="transition" name="no_transition" id="0x010f0000" />
<public type="transition" name="move" id="0x010f0001" />
<public type="transition" name="fade" id="0x010f0002" />
<public type="transition" name="explode" id="0x010f0003" />
<!-- type="transition" End -->
<public-group type="attr" first-id="0x01010569">
</public-group>
<public-group type="style" first-id="0x010302e0">
</public-group>
<public-group type="id" first-id="0x01020044">
</public-group>
<public-group type="string" first-id="0x0104001a">
</public-group>
</resources>